Mplus version 5.2 was used for these examples.
1.0 Descriptive statistics in Mplus
To indicate to Mplus that you want basic descriptive statistics (means, variances, covariances and correlations), you need to enter Type = basic; in the analysis command block. If you would like to be able to view histograms or scatterplots of some of your variables, you can add a plot command block. These types of univariate and bivariate graphs are plot1 types of graphs.
The data set is https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/hsb-1.dat .
Title:
Entering data example free format using https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/hsb-1.dat
Data:
File is "D:/https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/hsb-1.dat";
Variable:
Names are
id female race ses schtyp prog read write math science socst;
Usevariables are
id female race ses schtyp prog read write math science socst;
Analysis:
Type = basic;
Plot:
Type is plot1;
Here is the output that Mplus generates.
SUMMARY OF ANALYSIS
Number of groups 1
Number of observations 200
Number of dependent variables 11
Number of independent variables 0
Number of continuous latent variables 0
Observed dependent variables
Continuous
READ WRITE MATH ID FEMALE RACE
SES SCHTYP PROG SCIENCE SOCST
Estimator ML
Information matrix OBSERVED
Maximum number of iterations 1000
Convergence criterion 0.500D-04
Maximum number of steepest descent iterations 20
Input data file(s)
D:/https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/hsb-1.dat
Input data format FREE
RESULTS FOR BASIC ANALYSIS
SAMPLE STATISTICS
Means
READ WRITE MATH ID FEMALE
________ ________ ________ ________ ________
1 52.230 52.775 52.645 100.500 0.545
Means
RACE SES SCHTYP PROG SCIENCE
________ ________ ________ ________ ________
1 3.430 2.055 1.160 2.025 51.850
Means
SOCST
________
1 52.405
Covariances
READ WRITE MATH ID FEMALE
________ ________ ________ ________ ________
READ 105.123
WRITE 57.997 89.844
MATH 63.615 54.829 87.768
ID 88.196 102.420 118.877 3350.000
FEMALE -0.272 1.214 -0.137 -2.520 0.249
RACE 2.594 2.168 1.973 45.050 0.001
SES 2.178 1.424 1.849 8.842 -0.045
SCHTYP 0.325 0.443 0.338 10.261 0.003
PROG -0.956 -1.185 -0.971 -2.319 0.001
SCIENCE 63.969 53.534 58.504 184.181 -0.631
SOCST 68.409 61.544 54.763 113.902 0.281
Covariances
RACE SES SCHTYP PROG SCIENCE
________ ________ ________ ________ ________
RACE 1.081
SES 0.147 0.525
SCHTYP 0.041 0.036 0.135
PROG -0.036 0.009 -0.024 0.477
SCIENCE 3.296 2.028 0.235 -1.298 98.028
SOCST 2.121 2.581 0.382 -1.447 49.438
Covariances
SOCST
________
SOCST 115.257
Correlations
READ WRITE MATH ID FEMALE
________ ________ ________ ________ ________
READ 1.000
WRITE 0.597 1.000
MATH 0.662 0.617 1.000
ID 0.149 0.187 0.219 1.000
FEMALE -0.053 0.256 -0.029 -0.087 1.000
RACE 0.243 0.220 0.203 0.749 0.001
SES 0.293 0.207 0.272 0.211 -0.125
SCHTYP 0.086 0.127 0.098 0.482 0.015
PROG -0.135 -0.181 -0.150 -0.058 0.004
SCIENCE 0.630 0.570 0.631 0.321 -0.128
SOCST 0.621 0.605 0.544 0.183 0.052
Correlations
RACE SES SCHTYP PROG SCIENCE
________ ________ ________ ________ ________
RACE 1.000
SES 0.195 1.000
SCHTYP 0.108 0.137 1.000
PROG -0.050 0.017 -0.095 1.000
SCIENCE 0.320 0.283 0.065 -0.190 1.000
SOCST 0.190 0.332 0.097 -0.195 0.465
Correlations
SOCST
________
SOCST 1.000
PLOT INFORMATION
The following plots are available:
Histograms (sample values)
Scatterplots (sample values)
Beginning Time: 11:35:42
Ending Time: 11:35:43
Elapsed Time: 00:00:01
You can compare these summary statistics to those found in another software package or by hand to ensure that you have read the data into Mplus correctly. To view plots, you can select Graph, View graphs or press Alt-V to open the dialog box below.
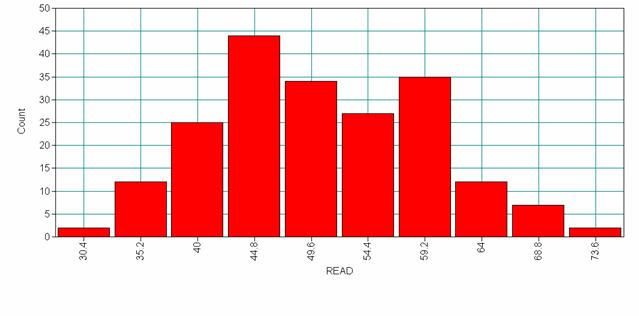
From here, you can select Histograms and choose read from the drop down menu to get the plot below.
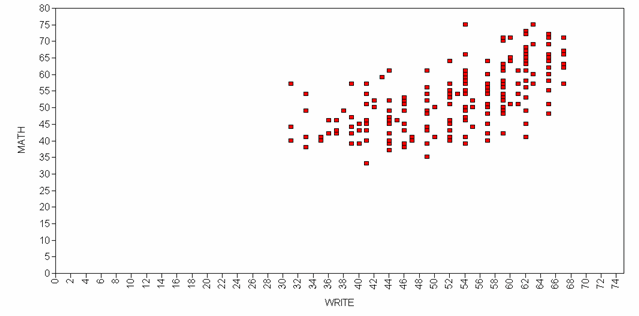
Alternatively, you can select Scatterplots and choose to look at math and write.
2.0 Descriptive statistics with missing data without listwise deletion
Next, we will look at a dataset with missing data. This time we will not include the id variable in the analyses. We will use the hsbmis.dat datafile and hsbmis.inp command file created by Stata in the previous section to demonstrate the descriptive statistics.
Data:
File is "D:hsbmis.dat" ;
Variable:
Names are
id female race ses schtyp prog read write math science socst;
Missing are all (-9999) ;
Usevariables are
female race ses schtyp prog read write math science socst;
Analysis:
type = basic missing ; ! note we added missing
Here is the output generated by Mplus.
SUMMARY OF ANALYSIS
Number of groups 1
Number of observations 200
Number of dependent variables 11
Number of independent variables 0
Number of continuous latent variables 0
Observed dependent variables
Continuous
ID FEMALE RACE SES SCHTYP PROG
READ WRITE MATH SCIENCE SOCST
Estimator ML
Information matrix OBSERVED
Maximum number of iterations 1000
Convergence criterion 0.500D-04
Maximum number of steepest descent iterations 20
Maximum number of iterations for H1 2000
Convergence criterion for H1 0.100D-03
Input data file(s)
D:hsbmis.dat
Input data format FREE
SUMMARY OF DATA
Number of missing data patterns 7
SUMMARY OF MISSING DATA PATTERNS
MISSING DATA PATTERNS (x = not missing)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
ID x x x x x x x
FEMALE x x x x x x
RACE x x x x x x x
SES x x x x x x x
SCHTYP x x x x x x x
PROG x x x x x x x
READ x x x x x x
WRITE x x x x x x
MATH x x x x x x
SCIENCE x x x x x x
SOCST x x x x x x
MISSING DATA PATTERN FREQUENCIES
Pattern Frequency Pattern Frequency Pattern Frequency
1 138 4 12 7 6
2 5 5 14
3 14 6 11
COVARIANCE COVERAGE OF DATA
Minimum covariance coverage value 0.100
PROPORTION OF DATA PRESENT
Covariance Coverage
ID FEMALE RACE SES SCHTYP
________ ________ ________ ________ ________
ID 1.000
FEMALE 0.970 0.970
RACE 1.000 0.970 1.000
SES 1.000 0.970 1.000 1.000
SCHTYP 1.000 0.970 1.000 1.000 1.000
PROG 1.000 0.970 1.000 1.000 1.000
READ 0.945 0.915 0.945 0.945 0.945
WRITE 0.930 0.900 0.930 0.930 0.930
MATH 0.940 0.910 0.940 0.940 0.940
SCIENCE 0.930 0.900 0.930 0.930 0.930
SOCST 0.975 0.945 0.975 0.975 0.975
Covariance Coverage
PROG READ WRITE MATH SCIENCE
________ ________ ________ ________ ________
PROG 1.000
READ 0.945 0.945
WRITE 0.930 0.875 0.930
MATH 0.940 0.885 0.870 0.940
SCIENCE 0.930 0.875 0.860 0.870 0.930
SOCST 0.975 0.920 0.905 0.915 0.905
Covariance Coverage
SOCST
________
SOCST 0.975
RESULTS FOR BASIC ANALYSIS
ESTIMATED SAMPLE STATISTICS
Means
ID FEMALE RACE SES SCHTYP
________ ________ ________ ________ ________
1 100.500 0.546 3.430 2.055 1.160
Means
PROG READ WRITE MATH SCIENCE
________ ________ ________ ________ ________
1 2.025 52.361 52.560 52.796 51.839
Means
SOCST
________
1 52.353
Covariances
ID FEMALE RACE SES SCHTYP
________ ________ ________ ________ ________
ID 3333.250
FEMALE -1.848 0.247
RACE 44.825 0.015 1.075
SES 8.797 -0.041 0.146 0.522
SCHTYP 10.210 0.002 0.041 0.036 0.134
PROG -2.308 0.008 -0.036 0.009 -0.024
READ 87.947 -0.281 2.622 2.285 0.350
WRITE 100.623 1.199 2.052 1.386 0.475
MATH 120.213 -0.249 2.086 1.680 0.240
SCIENCE 168.152 -0.602 3.084 1.861 0.290
SOCST 113.330 0.252 2.035 2.546 0.388
Covariances
PROG READ WRITE MATH SCIENCE
________ ________ ________ ________ ________
PROG 0.474
READ -0.964 104.529
WRITE -1.197 56.743 88.262
MATH -1.117 61.541 53.418 84.921
SCIENCE -1.456 63.739 54.726 58.634 94.130
SOCST -1.432 67.903 60.147 50.856 50.528
Covariances
SOCST
________
SOCST 115.411
Correlations
ID FEMALE RACE SES SCHTYP
________ ________ ________ ________ ________
ID 1.000
FEMALE -0.064 1.000
RACE 0.749 0.029 1.000
SES 0.211 -0.114 0.195 1.000
SCHTYP 0.482 0.013 0.108 0.137 1.000
PROG -0.058 0.023 -0.050 0.017 -0.095
READ 0.149 -0.055 0.247 0.309 0.093
WRITE 0.186 0.256 0.211 0.204 0.138
MATH 0.226 -0.054 0.218 0.252 0.071
SCIENCE 0.300 -0.125 0.307 0.265 0.082
SOCST 0.183 0.047 0.183 0.328 0.099
Correlations
PROG READ WRITE MATH SCIENCE
________ ________ ________ ________ ________
PROG 1.000
READ -0.137 1.000
WRITE -0.185 0.591 1.000
MATH -0.176 0.653 0.617 1.000
SCIENCE -0.218 0.643 0.600 0.656 1.000
SOCST -0.194 0.618 0.596 0.514 0.485
Correlations
SOCST
________
SOCST 1.000
MAXIMUM LOG-LIKELIHOOD VALUE FOR THE UNRESTRICTED (H1) MODEL IS -5102.296
Beginning Time: 11:56:08
Ending Time: 11:56:08
Elapsed Time: 00:00:00
Because we indicated that our data included missing values, our basic output included “SUMMARY OF MISSING DATA PATTERNS” in which we can see which combinations of variables are missing for how many observations in our data. From this section of output, we can see that we have 138 complete observations and no more than one missing variable in any of our other observations.
2.1 Descriptive statistics with missing data with listwise deletion
You might also notice that the descriptive statistics from Mplus do not match with the output from a standard statistics software package, such as SPSS, Stata or SAS, when missing data are present. This is because that by default Mplus uses the maximum likelihood estimation, and it uses all the available values instead of doing the listwise deletion, which is the default behavior in SPSS, Stata or SAS. For the purpose of checking data, you can request that Mplus does listwise deletion as well. Here is the syntax.
Data:
File is "D:hsbmis.dat" ;
listwise = on;
Variable:
Names are
id female race ses schtyp prog read write math science socst;
Missing are all (-9999) ;
Usevariables are
female race ses schtyp prog read write math science socst;
Analysis:
type = basic ;
