HLM Textbook Examples
Multilevel Analysis by Tom Snijders and Roel Bosker
Chapter 4: The Random Intercept Model
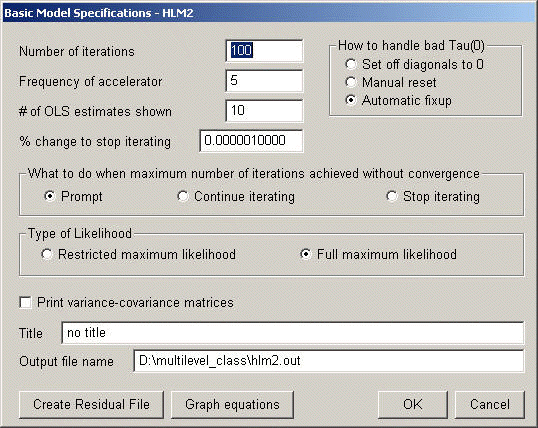
Example 4.1 on page 46-47 using https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/mlbook1.ssm. We use full maximum likelihood estimation method for this example. From Basic Model Specifications menu, choose Full maximum likelihood.
Final estimation of fixed effects
(with robust standard errors)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Standard Approx.
Fixed Effect Coefficient Error T-ratio d.f. P-value
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
For INTRCPT1, B0
INTRCPT2, G00 40.364049 0.426363 94.671 130 0.000
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Final estimation of variance components:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Random Effect Standard Variance df Chi-square P-value
Deviation Component
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
INTRCPT1, U0 4.40800 19.43043 130 733.95978 0.000
level-1, R 8.03540 64.56761
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Statistics for current covariance components model
--------------------------------------------------
Deviance = 16251.380618
Number of estimated parameters = 3
Example 4.2 on page 49-51 using the same data set as previous example. Notice that in this example, predictor variable IQ_VERB enters into the model as grand-mean centered. We still use full ML method in this example.
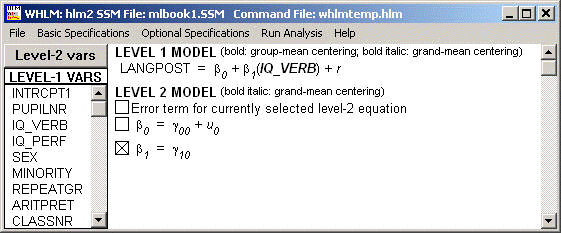
Final estimation of fixed effects:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Standard Approx.
Fixed Effect Coefficient Error T-ratio d.f. P-value
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
For INTRCPT1, B0
INTRCPT2, G00 40.609312 0.306915 132.315 130 0.000
For IQ_VERB slope, B1
INTRCPT2, G10 2.488070 0.070055 35.516 2285 0.000
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
The outcome variable is LANGPOST
Final estimation of fixed effects
(with robust standard errors)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Standard Approx.
Fixed Effect Coefficient Error T-ratio d.f. P-value
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
For INTRCPT1, B0
INTRCPT2, G00 40.609312 0.304860 133.206 130 0.000
For IQ_VERB slope, B1
INTRCPT2, G10 2.488070 0.080804 30.792 2285 0.000
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Final estimation of variance components:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Random Effect Standard Variance df Chi-square P-value
Deviation Component
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
INTRCPT1, U0 3.08179 9.49741 130 617.20294 0.000
level-1, R 6.49824 42.22709
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Statistics for current covariance components model
--------------------------------------------------
Deviance = 15249.935081
Number of estimated parameters = 4
We will skip Figure 4.2 here since HLM 5.05 does not produce this type of plots.
Table 4.3 Estimates for ordinary least squares regression.
The least-squares likelihood value = -7738.844160
Deviance = 15477.68832
Number of estimated parameters = 3
The outcome variable is LANGPOST
Least-squares estimates of fixed effects
(with robust standard errors)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Standard
Fixed Effect Coefficient Error T-ratio d.f. P-value
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
For INTRCPT1, B0
INTRCPT2, G00 40.934848 0.296554 138.035 2285 0.000
For IQ_VERB slope, B1
INTRCPT2, G10 2.653896 0.083866 31.645 2285 0.000
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
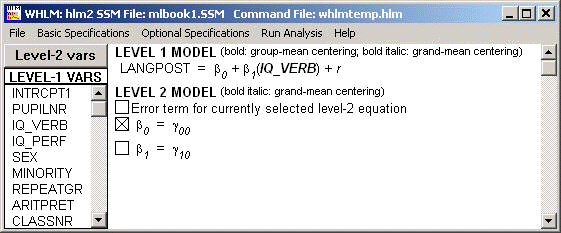
Example 4.3 on page 55. Level-1 variable IQ_VERB is entered as grand-mean centered. Level-2 variable IQ_VERB_ (which is the group mean of IQ_VERB) then is entered as grand-mean centered.
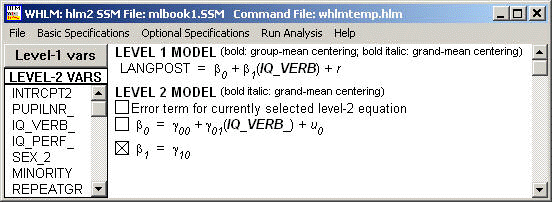
Final estimation of fixed effects:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Standard Approx.
Fixed Effect Coefficient Error T-ratio d.f. P-value
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
For INTRCPT1, B0
INTRCPT2, G00 40.540591 0.284164 142.666 129 0.000
IQ_VERB_, G01 1.588534 0.312758 5.079 129 0.000
For IQ_VERB slope, B1
INTRCPT2, G10 2.414772 0.071659 33.698 2284 0.000
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
The outcome variable is LANGPOST
Final estimation of fixed effects
(with robust standard errors)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Standard Approx.
Fixed Effect Coefficient Error T-ratio d.f. P-value
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
For INTRCPT1, B0
INTRCPT2, G00 40.540591 0.281984 143.769 129 0.000
IQ_VERB_, G01 1.588534 0.319648 4.970 129 0.000
For IQ_VERB slope, B1
INTRCPT2, G10 2.414772 0.085438 28.263 2284 0.000
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Final estimation of variance components:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Random Effect Standard Variance df Chi-square P-value
Deviation Component
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
INTRCPT1, U0 2.78015 7.72921 129 540.50513 0.000
level-1, R 6.49242 42.15150
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Statistics for current covariance components model
--------------------------------------------------
Deviance = 15225.710258
Number of estimated parameters = 5
