R Textbook Examples Applied Longitudinal Data Analysis: Modeling Change and Event Occurrence by Judith D. Singer and John B. Willett Chapter 4: Doing Data Analysis with the Multilevel Model for Change
#Read data and attach dataset
alcohol1 <- read.table("https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/stat/r/examples/alda/data/alcohol1_pp.txt", header=T, sep=",")
attach(alcohol1)
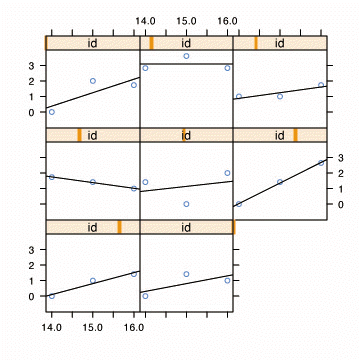
Fig. 4.1, p. 77. Empirical growth plots with superimposed OLS trajectories.
library(lattice)
xyplot(alcuse~age | id,
data=alcohol1[alcohol1$id %in% c(4, 14, 23, 32, 41, 56, 65, 82), ],
panel=function(x,y){
panel.xyplot(x, y)
panel.lmline(x,y)
}, ylim=c(-1, 4), as.table=T)
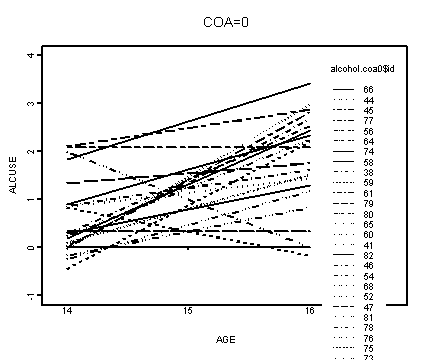
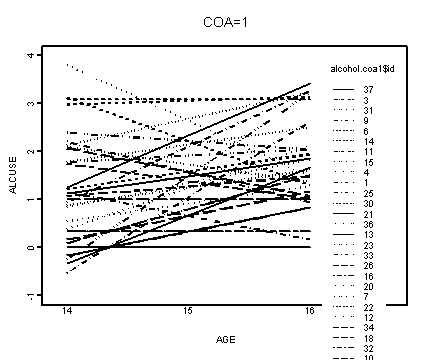
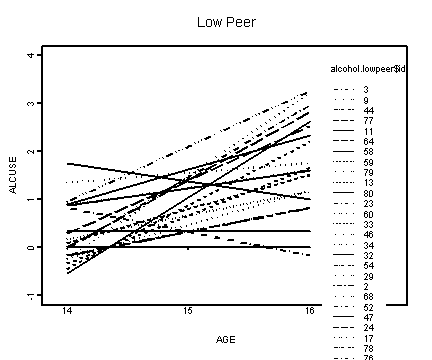
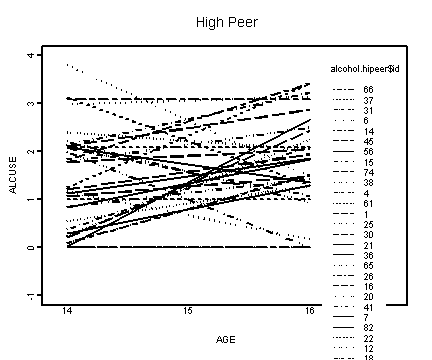
Fig. 4.2, p.79. Fitted OLS trajectories displayed separately by coa status and peer levels.
Upper left panel, coa=0.
alcohol.coa0 <- alcohol1[alcohol1$coa==0, ]
#fitting the linear model by id
f.coa0 <- by(alcohol.coa0, alcohol.coa0$id,
function(data) fitted(lm(alcuse~age, data=data)))
#transforming f.coa from a list to a vector and
#stripping of the names of the elements in the vector
f.coa0 <- unlist(f.coa0)
names(f.coa0) <- NULL
#plotting the linear fit by id
interaction.plot(alcohol.coa0$age, alcohol.coa0$id, f.coa0,
xlab="AGE", ylab="ALCUSE", ylim=c(-1, 4), lwd=1)
title("COA=0")
Upper right panel, coa=1.
alcohol.coa1 <- alcohol1[alcohol1$coa==1, ]
#fitting the linear model by id
f.coa1 <- by(alcohol.coa1, alcohol.coa1$id,
function(data) fitted(lm(alcuse~age, data=data)))
#transforming f.coa1 from a list to a vector and
#stripping of the names of the elements in the vector
f.coa1 <- unlist(f.coa1)
names(f.coa1) <- NULL
#plotting the linear fit by id
interaction.plot(alcohol.coa1$age, alcohol.coa1$id, f.coa1,
xlab="AGE", ylab="ALCUSE", ylim=c(-1, 4), lwd=1)
title("COA=1")
Obtaining the mean of peer and graphing the lower left panel, peer<=1.01756.
mean(alcohol1$peer)
[1] 1.01756
alcohol.lowpeer <- alcohol1[alcohol1$peer<=1.01756, ]
#fitting the linear model by id
f.lowpeer <- by(alcohol.lowpeer, alcohol.lowpeer$id,
function(data) fitted(lm(alcuse~age, data=data)))
#transforming f.lowpeer from a list to a vector and
#stripping of the names of the elements in the vector
f.lowpeer <- unlist(f.lowpeer)
names(f.lowpeer) <- NULL
#plotting the linear fit by id
interaction.plot(alcohol.lowpeer$age, alcohol.lowpeer$id, f.lowpeer,
xlab="AGE", ylab="ALCUSE", ylim=c(-1, 4), lwd=1)
title("Low Peer")
Lower right panel, peer>1.01756.
alcohol.hipeer <- alcohol1[alcohol1$peer>1.01756, ]
#fitting the linear model by id
f.hipeer <- by(alcohol.hipeer, alcohol.hipeer$id,
function(data) fitted(lm(alcuse~age, data=data)))
#transforming f.hipeer from a list to a vector and
#stripping of the names of the elements in the vector
f.hipeer <- unlist(f.hipeer)
names(f.hipeer) <- NULL
#plotting the linear fit by id
interaction.plot(alcohol.hipeer$age, alcohol.hipeer$id, f.hipeer,
xlab="AGE", ylab="ALCUSE", ylim=c(-1, 4), lwd=1)
title("High Peer")
Table 4.1, p. 94-95.
#Model A
library(nlme)
model.a <- lme(alcuse~ 1, alcohol1, random= ~1 |id)
summary(model.a)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by REML
Data: alcohol1
AIC BIC logLik
679.0049 689.5087 -336.5025
Random effects:
Formula: ~1 | id
(Intercept) Residual
StdDev: 0.7570578 0.7494974
Fixed effects: alcuse ~ 1
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 0.9219549 0.09629638 164 9.574139 0
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-1.8892070 -0.3079143 -0.3029178 0.6110925 2.8562135
Number of Observations: 246
Number of Groups: 82
#Model B
model.b <- lme(alcuse ~ age_14 , data=alcohol1, random= ~ age_14 | id, method="ML")
summary(model.b)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: alcohol1
AIC BIC logLik
648.6111 669.643 -318.3055
Random effects:
Formula: ~age_14 | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 0.7901617 (Intr)
age_14 0.3888470 -0.223
Residual 0.5807690
Fixed effects: alcuse ~ age_14
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 0.6513035 0.10551005 163 6.172905 0
age_14 0.2706514 0.06271014 163 4.315912 0
Correlation:
(Intr)
age_14 -0.441
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-2.47998885 -0.38401088 -0.07553389 0.39001356 2.50684931
Number of Observations: 246
Number of Groups: 82
#Model C
model.c <- lme(alcuse ~ coa*age_14 , data=alcohol1, random= ~ age_14 | id, method="ML")
summary(model.c)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: alcohol1
AIC BIC logLik
637.2026 665.2453 -310.6013
Random effects:
Formula: ~age_14 | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 0.6982690 (Intr)
age_14 0.3880684 -0.219
Residual 0.5807688
Fixed effects: alcuse ~ coa * age_14
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 0.3159517 0.13177099 162 2.397734 0.0176
coa 0.7432120 0.19616697 80 3.788671 0.0003
age_14 0.2929552 0.08492089 162 3.449742 0.0007
coa:age_14 -0.0494299 0.12642140 162 -0.390993 0.6963
Correlation:
(Intr) coa age_14
coa -0.672
age_14 -0.460 0.309
coa:age_14 0.309 -0.460 -0.672
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-2.5480533 -0.3879877 -0.1057547 0.3602391 2.3960739
Number of Observations: 246
Number of Groups: 82
#Model D
model.d <- lme(alcuse ~ coa*age_14+peer*age_14 , data=alcohol1, random= ~ age_14 | id, method="ML")
summary(model.d)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: alcohol1
AIC BIC logLik
608.6906 643.744 -294.3453
Random effects:
Formula: ~age_14 | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 0.4908199 (Intr)
age_14 0.3729821 -0.033
Residual 0.5807668
Fixed effects: alcuse ~ coa * age_14 + peer * age_14
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) -0.3165142 0.14990058 161 -2.111494 0.0363
coa 0.5791651 0.16450407 79 3.520673 0.0007
age_14 0.4294286 0.11510211 161 3.730849 0.0003
peer 0.6942956 0.11291811 79 6.148665 0.0000
coa:age_14 -0.0140319 0.12631549 161 -0.111086 0.9117
age_14:peer -0.1498150 0.08670489 161 -1.727873 0.0859
Correlation:
(Intr) coa age_14 peer c:g_14
coa -0.371
age_14 -0.436 0.162
peer -0.686 -0.162 0.299
coa:age_14 0.162 -0.436 -0.371 0.071
age_14:peer 0.299 0.071 -0.686 -0.436 -0.162
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-2.59555028 -0.40005029 -0.07769136 0.46002837 2.29373867
Number of Observations: 246
Number of Groups: 82
#Model E
model.e <- lme(alcuse ~ coa+peer*age_14 , data=alcohol1, random= ~ age_14 | id, method="ML")
summary(model.e)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: alcohol1
AIC BIC logLik
606.7033 638.2513 -294.3516
Random effects:
Formula: ~age_14 | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 0.4908384 (Intr)
age_14 0.3730386 -0.034
Residual 0.5807689
Fixed effects: alcuse ~ coa + peer * age_14
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) -0.3138215 0.14762315 162 -2.125828 0.0350
coa 0.5711970 0.14773604 79 3.866335 0.0002
peer 0.6951827 0.11240363 79 6.184699 0.0000
age_14 0.4246867 0.10667952 162 3.980958 0.0001
peer:age_14 -0.1513771 0.08538528 162 -1.772872 0.0781
Correlation:
(Intr) coa peer age_14
coa -0.338
peer -0.709 -0.146
age_14 -0.410 0.000 0.351
peer:age_14 0.334 0.000 -0.431 -0.814
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-2.5955443 -0.4041410 -0.0835195 0.4554950 2.2997515
Number of Observations: 246
Number of Groups: 82
#Model F
model.f <- lme(alcuse ~ coa+cpeer*age_14 , data=alcohol1, random= ~ age_14 | id, method="ML")
summary(model.f)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: alcohol1
AIC BIC logLik
606.7033 638.2513 -294.3516
Random effects:
Formula: ~age_14 | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 0.4908389 (Intr)
age_14 0.3730381 -0.034
Residual 0.5807690
Fixed effects: alcuse ~ coa + cpeer * age_14
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 0.3938745 0.10460706 162 3.765276 0.0002
coa 0.5711970 0.14773612 79 3.866333 0.0002
cpeer 0.6951827 0.11240368 79 6.184696 0.0000
age_14 0.2705847 0.06189978 162 4.371336 0.0000
cpeer:age_14 -0.1513771 0.08538523 162 -1.772873 0.0781
Correlation:
(Intr) coa cpeer age_14
coa -0.637
cpeer 0.094 -0.146
age_14 -0.336 0.000 0.000
cpeer:age_14 0.000 0.000 -0.431 0.001
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-2.59554441 -0.40414064 -0.08351877 0.45549526 2.29975184
Number of Observations: 246
Number of Groups: 82
#Model G
model.g <- lme(alcuse ~ ccoa+cpeer*age_14 , data=alcohol1, random= ~ age_14 | id, method="ML")
summary(model.g)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: alcohol1
AIC BIC logLik
606.7033 638.2513 -294.3516
Random effects:
Formula: ~age_14 | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 0.4908386 (Intr)
age_14 0.3730384 -0.034
Residual 0.5807690
Fixed effects: alcuse ~ ccoa + cpeer * age_14
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 0.6514843 0.08060971 162 8.081959 0.0000
ccoa 0.5711970 0.14773606 79 3.866334 0.0002
cpeer 0.6951827 0.11240365 79 6.184698 0.0000
age_14 0.2705847 0.06189981 162 4.371334 0.0000
cpeer:age_14 -0.1513771 0.08538526 162 -1.772872 0.0781
Correlation:
(Intr) ccoa cpeer age_14
ccoa 0.000
cpeer 0.001 -0.146
age_14 -0.436 0.000 0.000
cpeer:age_14 0.000 0.000 -0.431 0.001
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-2.59554430 -0.40414090 -0.08351925 0.45549506 2.29975158
Number of Observations: 246
Number of Groups: 82
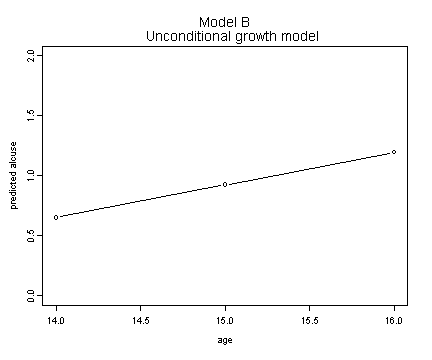
Fig. 4.3, p. 99. Model B
fixef.b <- fixef(model.b)
fit.b <- fixef.b[[1]] + alcohol1$age_14[1:3]*fixef.b[[2]]
plot(alcohol1$age[1:3], fit.b, ylim=c(0, 2), type="b",
ylab="predicted alcuse", xlab="age")
title("Model B \n Unconditional growth model")
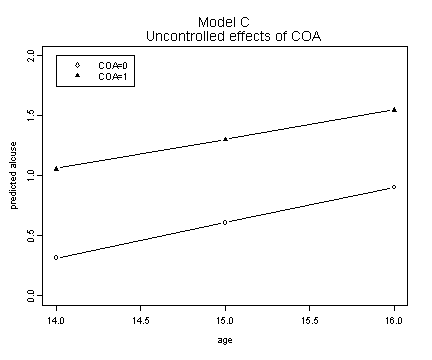
Model C.
fixef.c <- fixef(model.c)
fit.c0 <- fixef.c[[1]] + alcohol1$age_14[1:3]*fixef.c[[3]]
fit.c1 <- fixef.c[[1]] + fixef.c[[2]] +
alcohol1$age_14[1:3]*fixef.c[[3]] +
alcohol1$age_14[1:3]*fixef.c[[4]]
plot(alcohol1$age[1:3], fit.c0, ylim=c(0, 2), type="b",
ylab="predicted alcuse", xlab="age")
lines(alcohol1$age[1:3], fit.c1, type="b", pch=17)
title("Model C \n Uncontrolled effects of COA")
legend(14, 2, c("COA=0", "COA=1"))
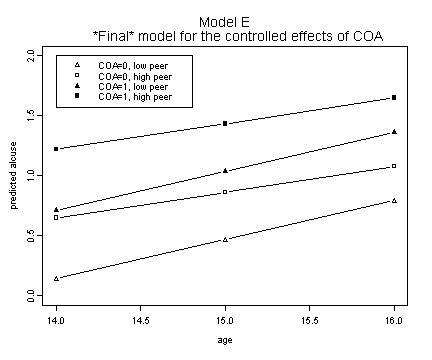
Model E.
fixef.e <- fixef(model.e)
fit.ec0p0 <- fixef.e[[1]] + .655*fixef.e[[3]] +
alcohol1$age_14[1:3]*fixef.e[[4]] +
.655*alcohol1$age_14[1:3]*fixef.e[[5]]
fit.ec0p1 <- fixef.e[[1]] + 1.381*fixef.e[[3]] +
alcohol1$age_14[1:3]*fixef.e[[4]] +
1.381*alcohol1$age_14[1:3]*fixef.e[[5]]
fit.ec1p0 <- fixef.e[[1]] + fixef.e[[2]] + .655*fixef.e[[3]] +
alcohol1$age_14[1:3]*fixef.e[[4]] +
.655*alcohol1$age_14[1:3]*fixef.e[[5]]
fit.ec1p1 <- fixef.e[[1]] + fixef.e[[2]] + 1.381*fixef.e[[3]] +
alcohol1$age_14[1:3]*fixef.e[[4]] +
1.381*alcohol1$age_14[1:3]*fixef.e[[5]]
plot(alcohol1$age[1:3], fit.ec0p0, ylim=c(0, 2), type="b",
ylab="predicted alcuse", xlab="age", pch=2)
lines(alcohol1$age[1:3], fit.ec0p1, type="b", pch=0)
lines(alcohol1$age[1:3], fit.ec1p0, type="b", pch=17)
lines(alcohol1$age[1:3], fit.ec1p1, type="b", pch=15)
title("Model E \n *Final* model for the controlled effects of COA")
legend(14, 2, c("COA=0, low peer", "COA=0, high peer",
"COA=1, low peer", "COA=1, high peer"))
Fig. 4.4–skipped
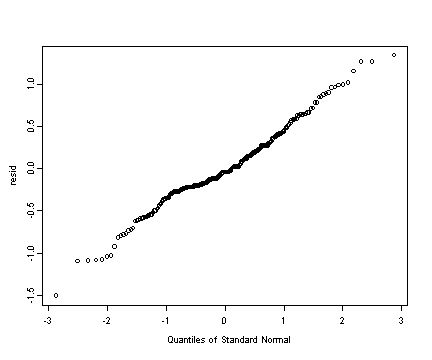
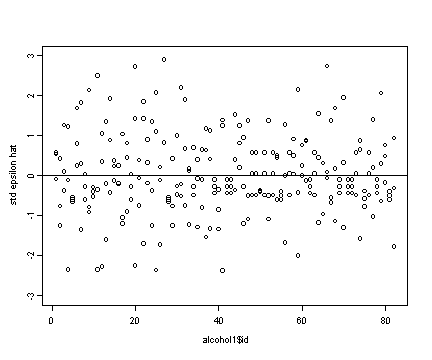
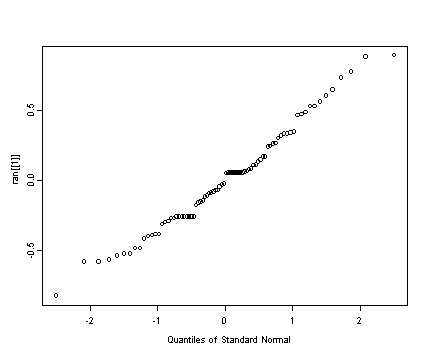
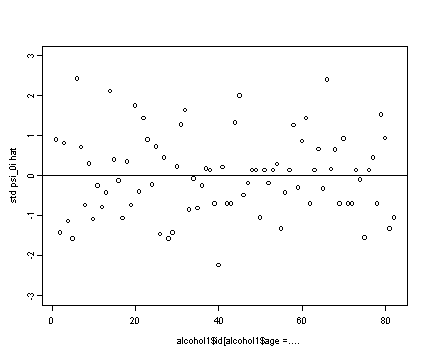
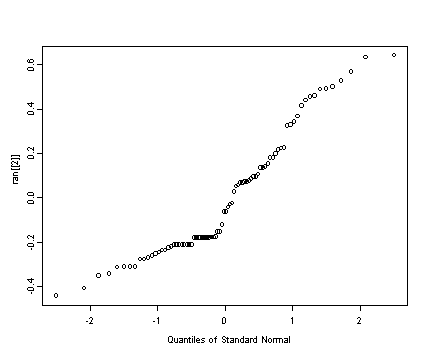
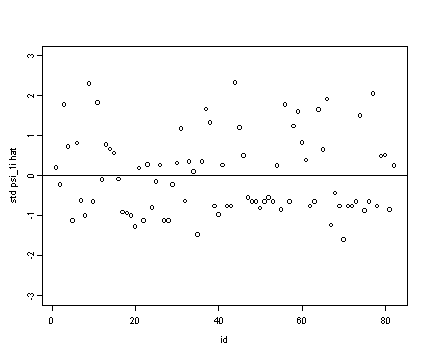
Fig. 4.5, p. 131. Normality assumption plots.
Upper left panel
#creating the residuals (epsilon.hat) resid <- residuals(model.f) qqnorm(resid)
Upper right panel
#creating the standardized residual (std epsilon.hat) resid.std <- resid/sd(resid) plot(alcohol1$id, resid.std, ylim=c(-3, 3), ylab="std epsilon hat") abline(h=0)
Middle left panel
#extracting the random effects of model f ran <- random.effects(model.f) qqnorm(ran[[1]])
Middle right panel
#standardizing the ksi0i.hat ran1.std <- ran[[1]]/sd(ran[[1]]) plot(alcohol1$id[alcohol1$age==14], ran1.std, ylim=c(-3, 3), ylab="std psi_0i hat") abline(h=0)
Lower left panel
qqnorm(ran[[2]])
Lower right panel
#standardizing the ksi1i.hat ran2.std <- ran[[2]]/sd(ran[[2]]) plot(id[alcohol1$age==14], ran2.std, ylim=c(-3, 3), ylab="std psi_1i hat") abline(h=0)
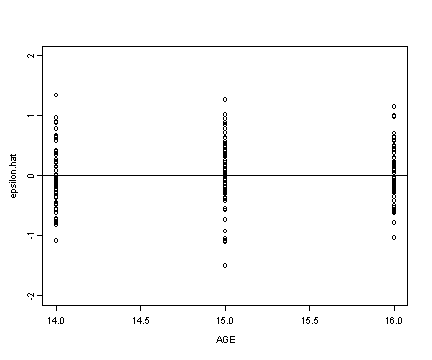
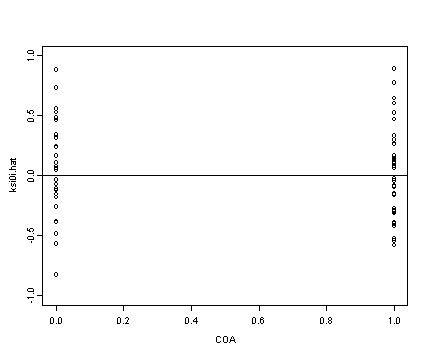
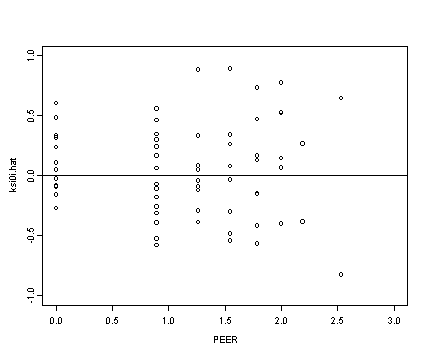
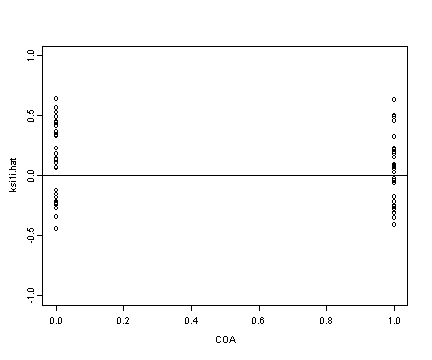
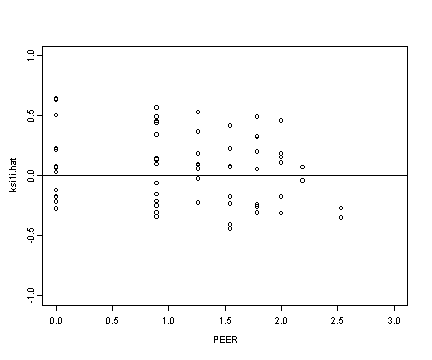
Fig. 4.6, p. 133. Homoscedasticity plots.
Upper panel
plot(alcohol1$age, resid, ylim=c(-2, 2), ylab="epsilon.hat",
xlab="AGE")
abline(h=0)
Middle left panel
plot(alcohol1$coa[alcohol1$age==14], ran[[1]], ylim=c(-1, 1),
ylab="ksi0i.hat", xlab="COA")
abline(h=0)
Middle right panel
plot(alcohol1$peer[alcohol1$age==14], ran[[1]], ylim=c(-1, 1),
xlim=c(0, 3), ylab="ksi0i.hat", xlab="PEER")
abline(h=0)
Lower left panel
plot(alcohol1$coa[alcohol1$age==14], ran[[2]], ylim=c(-1, 1),
ylab="ksi1i.hat", xlab="COA")
abline(h=0)
Lower right panel
plot(alcohol1$peer[alcohol1$age==14], ran[[2]], ylim=c(-1, 1),
xlim=c(0, 3), ylab="ksi1i.hat", xlab="PEER")
abline(h=0)