Applied Longitudinal Data Analysis: Modeling Change and Event Occurrence by Judith D. Singer and John B. Willett Chapter 5: Treating TIME More Flexibly
Inputting the reading data set.
reading <- read.table("https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/stat/r/examples/alda/data/reading_pp.txt", header=T, sep=",")
Table 5.1, p. 141.
reading[reading$id %in% c(4, 27, 31, 33, 41, 49, 69, 77, 87), ]
id wave agegrp age piat agegrp.c age.c
10 4 1 6.5 6.000000 18 0 -0.5000000
11 4 2 8.5 8.500000 31 2 2.0000000
12 4 3 10.5 10.666667 50 4 4.1666667
79 27 1 6.5 6.250000 19 0 -0.2500000
80 27 2 8.5 9.166667 36 2 2.6666667
81 27 3 10.5 10.916667 57 4 4.4166667
91 31 1 6.5 6.333333 18 0 -0.1666667
92 31 2 8.5 8.833333 31 2 2.3333333
93 31 3 10.5 10.916667 51 4 4.4166667
97 33 1 6.5 6.333333 18 0 -0.1666667
98 33 2 8.5 8.916667 34 2 2.4166667
99 33 3 10.5 10.750000 29 4 4.2500000
121 41 1 6.5 6.333333 18 0 -0.1666667
122 41 2 8.5 8.750000 28 2 2.2500000
123 41 3 10.5 10.833333 36 4 4.3333333
145 49 1 6.5 6.500000 19 0 0.0000000
146 49 2 8.5 8.750000 32 2 2.2500000
147 49 3 10.5 10.666667 48 4 4.1666667
205 69 1 6.5 6.666667 26 0 0.1666667
206 69 2 8.5 9.166667 47 2 2.6666667
207 69 3 10.5 11.333333 45 4 4.8333333
229 77 1 6.5 6.833333 17 0 0.3333333
230 77 2 8.5 8.083333 19 2 1.5833333
231 77 3 10.5 10.000000 28 4 3.5000000
259 87 1 6.5 6.916667 22 0 0.4166667
260 87 2 8.5 9.416667 49 2 2.9166667
261 87 3 10.5 11.500000 64 4 5.0000000
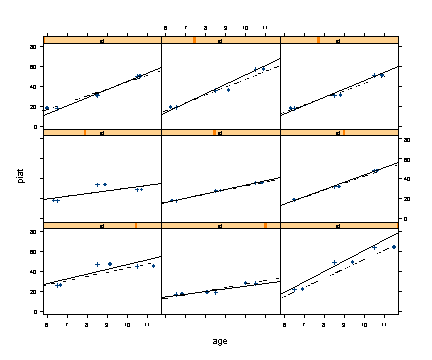
Fig. 5.1, p. 143. Empirical change plots with superimposed OLS trajectories. The +’s and solid lines correspond to time using the child’s target age at data collection, whereas the dots and dashed lines correspond to time using the child’s observed age.
library(lattice)
xyplot(piat~age | id,
data=reading[reading$id %in% c(4, 27, 31, 33, 41, 49, 69, 77, 87), ],
panel=function(x,y, subscripts){panel.xyplot(x, y, pch=16)
panel.lmline(x,y, lty=4)
panel.xyplot(reading$agegrp[subscripts], y, pch=3)
panel.lmline(reading$agegrp[subscripts],y) },
ylim=c(0, 80), as.table=T, subscripts=T)
Creating the centered variables called agegrp.c and age.c, p. 144.
mat2 <- reading[ ,3:4]-6.5
dimnames(mat2)[[2]] <- c("agegrp.c", "age.c")
reading <- cbind(reading, mat2)
Table 5.2, p. 145. Note: The degres of freedom used to in the calculations of the intercept is different from the results in the book and this difference in partitioning results also in slight differences in the standard error of the estimates.
#Using the agegrp variable.
library(nlme)
lme.agegrp <- lme(piat ~ agegrp.c, reading, random= ~ agegrp | id, method="ML")
summary(lme.agegrp)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: reading
AIC BIC logLik
1831.949 1853.473 -909.9746
Random effects:
Formula: ~agegrp | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 13.244933 (Intr)
agegrp 2.096994 -0.97
Residual 5.200308
Fixed effects: piat ~ agegrp.c
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 21.162921 0.6165805 177 34.32304 0
agegrp.c 5.030899 0.2967329 177 16.95430 0
Correlation:
(Intr)
agegrp.c -0.316
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-2.6585175 -0.5418435 -0.1434177 0.3871955 3.3133003
Number of Observations: 267
Number of Groups: 89
#Using the age variable.
lme.age <- lme(piat ~ age.c, reading, random= ~ age | id, method="ML")
summary(lme.age)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: reading
AIC BIC logLik
1815.896 1837.419 -901.9478
Random effects:
Formula: ~age | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 10.668937 (Intr)
age 1.816985 -0.985
Residual 5.238946
Fixed effects: piat ~ age.c
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 21.060816 0.5614177 177 37.51363 0
age.c 4.540021 0.2616162 177 17.35375 0
Correlation:
(Intr)
age.c -0.287
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-3.0068407 -0.4948682 -0.1369712 0.4095972 3.7274111
Number of Observations: 267
Number of Groups: 89
Inputting the wages data set.
wages <- read.table("https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/stat/r/examples/alda/data/wages_pp.txt", header=T, sep=",")
Table 5.3, p. 147.
wages[wages$id %in% c(206, 332, 1028), c(1, 3, 2, 6, 8, 10)]
id exper lnw black hgc uerate
75 206 1.874 2.028 0 10 9.200
76 206 2.814 2.297 0 10 11.000
77 206 4.314 2.482 0 10 6.295
197 332 0.125 1.630 0 8 7.100
198 332 1.625 1.476 0 8 9.600
199 332 2.413 1.804 0 8 7.200
200 332 3.393 1.439 0 8 6.195
201 332 4.470 1.748 0 8 5.595
202 332 5.178 1.526 0 8 4.595
203 332 6.082 2.044 0 8 4.295
204 332 7.043 2.179 0 8 3.395
205 332 8.197 2.186 0 8 4.395
206 332 9.092 4.035 0 8 6.695
466 1028 0.004 0.872 1 8 9.300
467 1028 0.035 0.903 1 8 7.400
468 1028 0.515 1.389 1 8 7.300
469 1028 1.483 2.324 1 8 7.400
470 1028 2.141 1.484 1 8 6.295
471 1028 3.161 1.705 1 8 5.895
472 1028 4.103 2.343 1 8 6.900
Table 5.4, p. 149.
#Model A
model.a <- lme(lnw~exper, wages, random= ~exper | id, method="ML")
summary(model.a)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: wages
AIC BIC logLik
4933.394 4973.98 -2460.697
Random effects:
Formula: ~exper | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 0.23295542 (Intr)
exper 0.04154474 -0.301
Residual 0.30839044
Fixed effects: lnw ~ exper
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 1.7156039 0.010798215 5513 158.87848 0
exper 0.0456807 0.002341936 5513 19.50555 0
Correlation:
(Intr)
exper -0.565
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-4.20113322 -0.52073077 -0.03159151 0.44063202 7.03696490
Number of Observations: 6402
Number of Groups: 888
#Model B
model.b <- update(model.a, lnw~exper*hgc.9+exper*black)
summary(model.b)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: wages
AIC BIC logLik
4893.751 4961.395 -2436.876
Random effects:
Formula: ~exper | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 0.22748211 (Intr)
exper 0.04044512 -0.31
Residual 0.30853484
Fixed effects: lnw ~ exper + hgc.9 + black + exper:hgc.9 + exper:black
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 1.7171385 0.012548264 5511 136.84271 0.0000
exper 0.0493428 0.002632917 5511 18.74074 0.0000
hgc.9 0.0349201 0.007885174 885 4.42858 0.0000
black 0.0153954 0.023937728 885 0.64315 0.5203
exper:hgc.9 0.0012794 0.001723983 5511 0.74213 0.4580
exper:black -0.0182129 0.005501727 5511 -3.31040 0.0009
Correlation:
(Intr) exper hgc.9 black exp:.9
exper -0.575
hgc.9 0.071 -0.020
black -0.523 0.301 -0.020
exper:hgc.9 -0.019 -0.003 -0.578 0.011
exper:black 0.275 -0.478 0.011 -0.573 -0.023
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-4.26907899 -0.51809173 -0.03347663 0.44516366 7.01940012
Number of Observations: 6402
Number of Groups: 888
#Model C
model.c <- update(model.b, lnw~exper+exper:black+hgc.9)
summary(model.c)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: wages
AIC BIC logLik
4890.704 4944.818 -2437.352
Random effects:
Formula: ~exper | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 0.22766404 (Intr)
exper 0.04057939 -0.312
Residual 0.30850207
Fixed effects: lnw ~ exper + hgc.9 + exper:black
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 1.7214750 0.010700480 5512 160.87830 0e+00
exper 0.0488470 0.002514196 5512 19.42849 0e+00
hgc.9 0.0383608 0.006435380 886 5.96092 0e+00
exper:black -0.0161150 0.004512766 5512 -3.57099 4e-04
Correlation:
(Intr) exper hgc.9
exper -0.515
hgc.9 0.077 -0.023
exper:black -0.036 -0.391 -0.015
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-4.27879296 -0.51825126 -0.03471525 0.44262176 7.01696754
Number of Observations: 6402
Number of Groups: 888
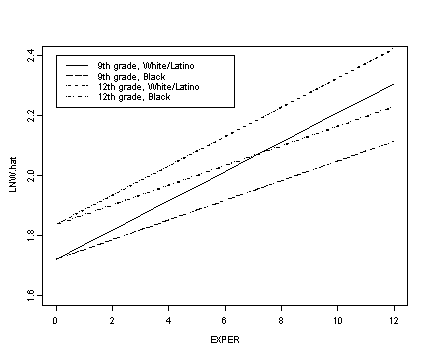
Fig. 5.2, p. 150. Log wage trajectories for four prototypical dropouts from model C.
exper.seq <- seq(0, 12)
fixef.c <- fixef(model.c)
x.w9 <- fixef.c[[1]] + fixef.c[[2]]*exper.seq
x.w12 <- fixef.c[[1]] + fixef.c[[2]]*exper.seq + fixef.c[[3]]*3
x.b9 <- fixef.c[[1]] + fixef.c[[2]]*exper.seq + fixef.c[[4]]*exper.seq
x.b12 <- fixef.c[[1]] + fixef.c[[2]]*exper.seq + fixef.c[[3]]*3 +
fixef.c[[4]]*exper.seq
plot(exper.seq, x.w9, ylim=c(1.6, 2.4), ylab="LNW.hat", xlab="EXPER", type="l", lwd=2)
lines(exper.seq, x.w12, lty=3)
lines(exper.seq, x.b9, lty=4, lwd=2)
lines(exper.seq, x.b12, lty=5)
legend(0, 2.4, c("9th grade, White/Latino", "9th grade, Black",
"12th grade, White/Latino", "12th grade, Black"), lty=c(1, 4, 3, 5))
Inputting the small wages data set.
wages.small <- read.table("https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/stat/r/examples/alda/data/wages_small_pp.txt", header=T, sep=",")
Table 5.5, p. 154.
#Model A
model.a <- lme(lnw~exper+hcg.9+exper:black, wages.small, random= ~exper|id, method="ML")
summary(model.a)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: wages.small
AIC BIC logLik
299.8772 328.2698 -141.9386
Random effects:
Formula: ~exper | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 2.902591e-01 (Intr)
exper 1.924436e-05 0
Residual 3.388214e-01
Fixed effects: lnw ~ exper + hcg.9 + exper:black
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 1.7373442 0.04812692 131 36.09921 0.0000
exper 0.0517798 0.02109799 131 2.45425 0.0154
hcg.9 0.0457585 0.02468875 122 1.85342 0.0662
exper:black -0.0600723 0.03485043 131 -1.72372 0.0871
Correlation:
(Intr) exper hcg.9
exper -0.614
hcg.9 0.051 -0.135
exper:black -0.130 -0.294 0.024
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-2.42021834 -0.47223444 -0.02901367 0.41970660 4.24393911
Number of Observations: 257
Number of Groups: 124
Inputting the unemployment data set.
unemployment <- read.table("https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/stat/r/examples/alda/data/unemployment_pp.txt", header=T, sep=","
Table 5.6, p. 161.
unemployment[unemployment$id %in% c(7589, 55697, 67641, 65441, 53782),]
id months cesd unemp
212 7589 1.3141684 36 1
213 7589 5.0924025 40 1
214 7589 11.7946612 39 1
454 53782 0.4271047 22 1
455 53782 4.2381930 15 0
456 53782 11.0718686 21 1
504 55697 1.3470226 7 1
505 55697 5.7823409 4 1
623 65441 1.0841889 27 1
624 65441 4.6981520 15 1
625 65441 11.2689938 7 0
647 67641 0.3285421 32 1
648 67641 4.1067762 9 0
649 67641 10.9404517 10 0
Table 5.7, p. 163.
#Model A
model.a <- lme(cesd ~ months, unemployment, random= ~months|id, method="ML")
summary(model.a)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: unemployment
AIC BIC logLik
5145.137 5172.217 -2566.569
Random effects:
Formula: ~months | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 9.3192519 (Intr)
months 0.5958468 -0.551
Residual 8.2975997
Fixed effects: cesd ~ months
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 17.669363 0.7767173 419 22.748768 0
months -0.421994 0.0831023 419 -5.078006 0
Correlation:
(Intr)
months -0.632
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-1.9978128 -0.5415801 -0.1608097 0.4454676 3.5519839
Number of Observations: 674
Number of Groups: 254
#Model B
model.b <- update(model.a, cesd~months+unemp)
summary(model.b)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: unemployment
AIC BIC logLik
5121.603 5153.196 -2553.802
Random effects:
Formula: ~months | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 9.6705179 (Intr)
months 0.6816912 -0.591
Residual 7.8985868
Fixed effects: cesd ~ months + unemp
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 12.665598 1.2448444 418 10.174443 0.0000
months -0.201984 0.0935246 418 -2.159683 0.0314
unemp 5.111304 0.9910522 418 5.157451 0.0000
Correlation:
(Intr) months
months -0.715
unemp -0.780 0.459
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-1.9609557 -0.5357110 -0.1191791 0.4303300 3.6857126
Number of Observations: 674
Number of Groups: 254
#Model C
model.c <- update(model.b, cesd~months*unemp)
summary(model.c)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: unemployment
AIC BIC logLik
5119.047 5155.153 -2551.523
Random effects:
Formula: ~months | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 9.6805554 (Intr)
months 0.6717203 -0.596
Residual 7.8759886
Fixed effects: cesd ~ months + unemp + months:unemp
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 9.616744 1.8949397 417 5.074961 0.0000
months 0.162036 0.1942395 417 0.834207 0.4046
unemp 8.529059 1.8834713 417 4.528372 0.0000
months:unemp -0.465222 0.2178620 417 -2.135398 0.0333
Correlation:
(Intr) months unemp
months -0.888
unemp -0.911 0.863
months:unemp 0.755 -0.878 -0.852
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-2.0039251 -0.5237204 -0.1548188 0.4308929 3.6960920
Number of Observations: 674
Number of Groups: 254
#Model D
model.d <- lme(cesd~unemp+unemp:months, unemployment, random=~unemp+unemp:months|id, control = list(optimizer = "nlm", msMaxIter = 100))
summary(model.d)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by REML
Data: unemployment
AIC BIC logLik
5115.584 5160.672 -2547.792
Random effects:
Formula: ~unemp + unempmonths | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 6.7650112 (Intr) unemp
unemp 6.7760936 0.133
unempmonths 0.8738672 0.120 -0.967
Residual 7.6874318
Fixed effects: cesd ~ unemp + unempmonths
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 11.197931 0.7925828 418 14.128405 0.0000
unemp 6.924134 0.9332866 418 7.419086 0.0000
unempmonths -0.303037 0.1124419 418 -2.695056 0.0073
Correlation:
(Intr) unemp
unemp -0.564
unempmonths -0.072 -0.444
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-2.1280241 -0.4893635 -0.1558296 0.4256349 3.7748883
Number of Observations: 674
Number of Groups: 254
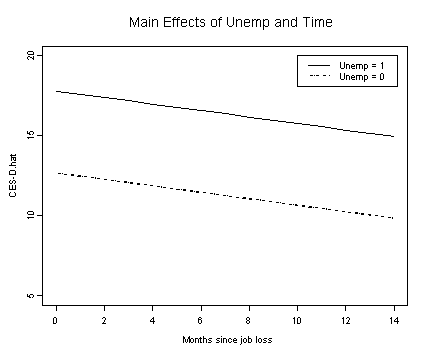
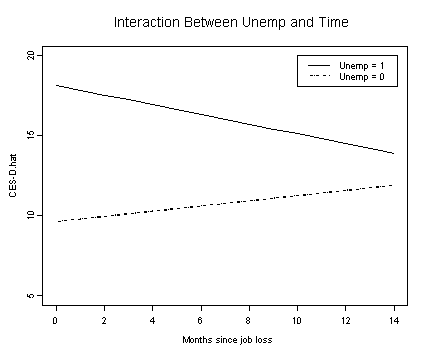
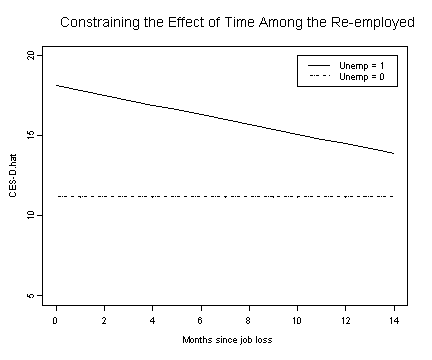
Fig. 5.4, p. 167.
#model B
fixef.b <- fixef(model.b)
months.seq <- seq(0, 14)
unemp.b1 <- fixef.b[[1]] + fixef.b[[2]]*months.seq + fixef.b[[3]]
unemp.b0 <- fixef.b[[1]] + fixef.b[[2]]*months.seq
plot(months.seq, unemp.b1, type="l", ylim=c(5, 20), ylab="CES-D.hat",
xlab="Months since job loss")
lines(months.seq, unemp.b0, lty=3)
legend(10, 20, c("Unemp = 1", "Unemp = 0"), lty=c(1, 3))
title("Main Effects of Unemp and Time")
#model C
fixef.c <- fixef(model.c)
unemp.c1 <- fixef.c[[1]] + fixef.c[[2]]*months.seq + fixef.c[[3]] +
fixef.c[[4]]*months.seq
unemp.c0 <- fixef.c[[1]] + fixef.c[[2]]*months.seq
plot(months.seq, unemp.c1, type="l", ylim=c(5, 20), ylab="CES-D.hat",
xlab="Months since job loss")
lines(months.seq, unemp.c0, lty=3)
legend(10, 20, c("Unemp = 1", "Unemp = 0"), lty=c(1, 3))
title("Interaction Between Unemp and Time"
#model D
fixef.d <- fixef(model.d)
unemp.d1 <- fixef.d[[1]] + fixef.d[[3]]*months.seq + fixef.d[[2]]
unemp.d0 <- rep(fixef.d[[1]], 15)
plot(months.seq, unemp.d1, type="l", ylim=c(5, 20), ylab="CES-D.hat",
xlab="Months since job loss")
lines(months.seq, unemp.d0, lty=3)
legend(10, 20, c("Unemp = 1", "Unemp = 0"), lty=c(1, 3))
title("Constraining the Effect of Time Among the Re-employed")
#Model A
model.a <- lme(lnw~hgc.9+ue.7+exper+exper:black, wages,
random=~exper|id, method="ML")
summary(model.a)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: wages
AIC BIC logLik
4848.519 4909.398 -2415.260
Random effects:
Formula: ~exper | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 0.22502612 (Intr)
exper 0.04039467 -0.32
Residual 0.30788820
Fixed effects: lnw ~ hgc.9 + ue.7 + exper + exper:black
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 1.7489885 0.011403780 5511 153.36920 0e+00
hgc.9 0.0400110 0.006365174 886 6.28592 0e+00
ue.7 -0.0119504 0.001792332 5511 -6.66753 0e+00
exper 0.0440539 0.002604399 5511 16.91517 0e+00
exper:black -0.0181832 0.004485454 5511 -4.05382 1e-04
Correlation:
(Intr) hgc.9 ue.7 exper
hgc.9 0.086
ue.7 -0.363 -0.039
exper -0.566 -0.033 0.277
exper:black -0.059 -0.018 0.070 -0.354
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-4.34080735 -0.51984995 -0.03652662 0.44253148 6.97854580
Number of Observations: 6402
Number of Groups: 888
#Model B
model.b <- update(model.a, lnw~hgc.9+ue.mean+ue.person.cen+exper+exper:black)
summary(model.b)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: wages
AIC BIC logLik
4846.978 4914.622 -2413.489
Random effects:
Formula: ~exper | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 0.22585733 (Intr)
exper 0.04035594 -0.332
Residual 0.30789898
Fixed effects: lnw ~ hgc.9 + ue.mean + ue.person.cen + exper + exper:black
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 1.8742603 0.029537336 5511 63.45394 0
hgc.9 0.0401695 0.006353674 885 6.32225 0
ue.mean -0.0177091 0.003521834 885 -5.02838 0
ue.person.cen -0.0099015 0.002098270 5511 -4.71890 0
exper 0.0450568 0.002651050 5511 16.99581 0
exper:black -0.0188696 0.004478998 5511 -4.21290 0
Correlation:
(Intr) hgc.9 ue.men u.prs. exper
hgc.9 0.058
ue.mean -0.926 -0.029
ue.person.cen -0.097 -0.027 -0.013
exper -0.187 -0.031 -0.030 0.334
exper:black -0.112 -0.019 0.105 0.018 -0.360
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-4.34617259 -0.51627687 -0.03591788 0.44100810 7.00029539
Number of Observations: 6402
Number of Groups: 888
#Model C
model.c <- update(model.b, lnw~hgc.9+ue1+ue.centert1+exper+exper:black)
summary(model.c)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: wages
AIC BIC logLik
4845.842 4913.485 -2412.921
Random effects:
Formula: ~exper | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 0.22422643 (Intr)
exper 0.04044107 -0.32
Residual 0.30784190
Fixed effects: lnw ~ hgc.9 + ue1 + ue.centert1 + exper + exper:black
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 1.8693452 0.026043822 5511 71.77691 0
hgc.9 0.0399276 0.006352135 885 6.28570 0
ue1 -0.0161774 0.002649638 885 -6.10551 0
ue.centert1 -0.0103090 0.001945368 5511 -5.29926 0
exper 0.0447649 0.002626143 5511 17.04588 0
exper:black -0.0183238 0.004486916 5511 -4.08383 0
Correlation:
(Intr) hgc.9 ue1 u.cnt1 exper
hgc.9 0.053
ue1 -0.913 -0.022
ue.centert1 -0.335 -0.038 0.335
exper -0.296 -0.033 0.093 0.302
exper:black -0.069 -0.018 0.058 0.059 -0.353
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-4.33611513 -0.51751018 -0.03512461 0.44130726 6.99734177
Number of Observations: 6402
Number of Groups: 888
Inputting the medication data set.
medication <- read.table("https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/stat/r/examples/alda/data/medication_pp.txt", header=T, sep=",")
Table 5.9, p. 182.
medication[c(1:6, 11, 16:21), c(3:8)] wave day time.of.day time time333 time667 1 1 0 0.0000000 0.0000000 -3.333333 -6.6666667 2 2 0 0.3333333 0.3333333 -3.000000 -6.3333333 3 3 0 0.6666667 0.6666667 -2.666667 -6.0000000 4 4 1 0.0000000 1.0000000 -2.333333 -5.6666667 5 5 1 0.3333333 1.3333333 -2.000000 -5.3333333 6 6 1 0.6666667 1.6666667 -1.666667 -5.0000000 11 11 3 0.3333333 3.3333333 0.000000 -3.3333333 16 16 5 0.0000000 5.0000000 1.666667 -1.6666667 17 17 5 0.3333333 5.3333333 2.000000 -1.3333333 18 19 6 0.0000000 6.0000000 2.666667 -0.6666667 19 20 6 0.3333333 6.3333333 3.000000 -0.3333333 20 21 6 0.6666667 6.6666667 3.333333 0.0000000 21 1 0 0.0000000 0.0000000 -3.333333 -6.6666667
Table 5.10, p. 184.
#Using time (Model A)
model.a <- lme(pos~treat*time, medication, random= ~time|id, method="ML")
summary(model.a)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: medication
AIC BIC logLik
12696.45 12737.45 -6340.226
Random effects:
Formula: ~time | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 45.949935 (Intr)
time 7.983475 -0.332
Residual 35.070353
Fixed effects: pos ~ treat * time
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 167.46346 9.341307 1176 17.927198 0.0000
treat -3.10930 12.352456 62 -0.251715 0.8021
time -2.41813 1.733646 1176 -1.394822 0.1633
treat:time 5.53681 2.281523 1176 2.426805 0.0154
Correlation:
(Intr) treat time
treat -0.756
time -0.404 0.305
treat:time 0.307 -0.408 -0.760
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-3.2708599 -0.4899446 -0.1174939 0.4240840 5.6180036
Number of Observations: 1242
Number of Groups: 64
#Using time - 3.33 (Model B)
model.b <- update(model.a, pos~treat*time333)
summary(model.b)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: medication
AIC BIC logLik
12696.45 12737.45 -6340.226
Random effects:
Formula: ~time | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 45.949935 (Intr)
time 7.983475 -0.332
Residual 35.070353
Fixed effects: pos ~ treat + time333 + treat:time333
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 159.40304 8.778656 1176 18.158023 0.0000
treat 15.34674 11.563284 62 1.327196 0.1893
time333 -2.41813 1.733646 1176 -1.394822 0.1633
treat:time333 5.53681 2.281523 1176 2.426805 0.0154
Correlation:
(Intr) treat tim333
treat -0.759
time333 0.229 -0.174
treat:time333 -0.174 0.222 -0.760
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-3.2708599 -0.4899446 -0.1174939 0.4240840 5.6180036
Number of Observations: 1242
Number of Groups: 64
#Using time - 6.67 (Model C)
model.c <- update(model.b, pos~treat*time667)
summary(model.c)
Linear mixed-effects model fit by maximum likelihood
Data: medication
AIC BIC logLik
12696.45 12737.45 -6340.226
Random effects:
Formula: ~time | id
Structure: General positive-definite, Log-Cholesky parametrization
StdDev Corr
(Intercept) 45.949935 (Intr)
time 7.983475 -0.332
Residual 35.070353
Fixed effects: pos ~ treat + time667 + treat:time667
Value Std.Error DF t-value p-value
(Intercept) 151.34261 11.561102 1176 13.090673 0.0000
treat 33.80278 15.182565 62 2.226421 0.0296
time667 -2.41813 1.733646 1176 -1.394822 0.1633
treat:time667 5.53681 2.281523 1176 2.426805 0.0154
Correlation:
(Intr) treat tim667
treat -0.761
time667 0.673 -0.513
treat:time667 -0.512 0.670 -0.760
Standardized Within-Group Residuals:
Min Q1 Med Q3 Max
-3.2708599 -0.4899446 -0.1174939 0.4240840 5.6180036
Number of Observations: 1242
Number of Groups: 64
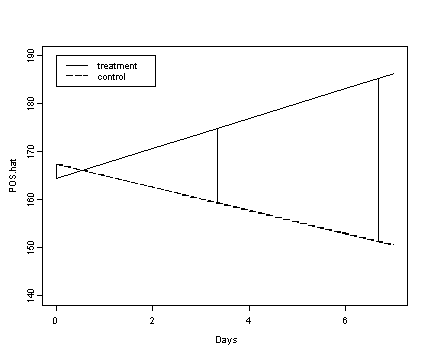
Fig. 5.5, p. 185. Note: The vertical lines reflect the magnitude of the effect of treatment when time is centered at different values.
days.seq <- seq(0, 7)
fixef.a <- fixef(model.a)
trt <- fixef.a[[1]] + fixef.a[[2]] + (fixef.a[[3]]+fixef.a[[4]])*days.seq
cnt <- fixef.a[[1]] + fixef.a[[3]]*days.seq
plot(days.seq, trt, ylim=c(140, 190), xlim=c(0, 7), type="l",
xlab="Days", ylab="POS.hat")
lines(days.seq, cnt, lty=4)
legend(0, 190, c("treatment", "control"), lty=c(1, 4))
segments(0, fixef.a[[1]] + fixef.a[[3]]*0, 0,
fixef.a[[1]] + fixef.a[[2]] + (fixef.a[[3]]+fixef.a[[4]])*0)
segments(3.33, fixef.a[[1]] + fixef.a[[3]]*3.33, 3.33,
fixef.a[[1]] + fixef.a[[2]] + (fixef.a[[3]]+fixef.a[[4]])*3.33)
segments(6.670, fixef.a[[1]] + fixef.a[[3]]*6.670, 6.670,
fixef.a[[1]] + fixef.a[[2]] + (fixef.a[[3]]+fixef.a[[4]])*6.670)