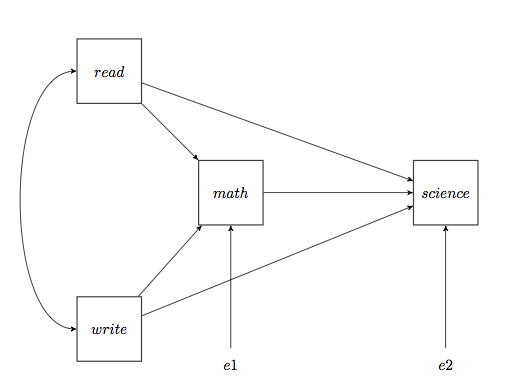
It is possible to estimate recursive path models using ordinary least squares regression, but using the SAS proc calis can make the processes easier and will also provide estimates of direct and indirect effects.
Let’s say that we want to estimate the following path model using the hsb2 (hsb2.sas7bdat) dataset.
We will begin computing the correlation between the two exogenous variables, read and write. We assume that the data file, hsb2.sas7bdat, is located in the data directory on the C: drive. You may need to change these values for your particular computer configuration.
proc corr data='C:datahsb2';
var read write;
run;
The CORR Procedure
2 Variables: READ WRITE
Simple Statistics
Variable N Mean Std Dev Sum Minimum Maximum Label
READ 200 52.23000 10.25294 10446 28.00000 76.00000 reading score
WRITE 200 52.77500 9.47859 10555 31.00000 67.00000 writing score
Pearson Correlation Coefficients, N = 200
Prob > |r| under H0: Rho=0
READ WRITE
READ 1.00000 0.59678
reading score <.0001
WRITE 0.59678 1.00000
writing score <.0001
This path analysis is really just two regression models. The first model is math = constant + read + write while the second model is science = constant + math + read + write. In proc calis we set up the model by entering the response variable with each predictor. In the effpart part of the command we list the paths for direct and indirect effects.
proc calis data='C:datahsb2'; path /* specification of path model */ science <- math , science <- read , science <- write, math <- read , math <- write; effpart /* for direct and indirect effects */ science <- read write; run;
We can now run the proc calis command which produces the output shown below. There is a lot of output but we will be focusing on the standardized results given near the end and shown in bold.
The CALIS Procedure
Covariance Structure Analysis: Model and Initial Values
Modeling Information
Data Set WC000001.HSB2
N Records Read 200
N Records Used 200
N Obs 200
Model Type PATH
Analysis Covariances
Variables in the Model
Endogenous Manifest MATH SCIENCE
Latent
Exogenous Manifest READ WRITE
Latent
Number of Endogenous Variables = 2
Number of Exogenous Variables = 2
Initial Estimates for PATH List
----------Path---------- Parameter Estimate
SCIENCE <--- MATH _Parm1 .
SCIENCE <--- READ _Parm2 .
SCIENCE <--- WRITE _Parm3 .
MATH <--- READ _Parm4 .
MATH <--- WRITE _Parm5 .
Initial Estimates for Variance Parameters
Variance
Type Variable Parameter Estimate
Exogenous READ _Add1 .
WRITE _Add2 .
Error MATH _Add3 .
SCIENCE _Add4 .
WRITE READ _Add5 .
NOTE: Parameters with prefix '_Add' are added by PROC CALIS.
Simple Statistics
Variable Mean Std Dev
READ reading score 52.23000 10.25294
WRITE writing score 52.77500 9.47859
MATH math score 52.64500 9.36845
SCIENCE science score 51.85000 9.90089
The SAS System 08:25
Thursday, May 12, 2011 180
The CALIS Procedure
Covariance Structure Analysis: Optimization
Initial Estimation Methods
1 Observed Moments of Variables
2 McDonald Method
3 Two-Stage Least Squares
Optimization Start
Parameter Estimates
N Parameter Estimate Gradient
1 _Parm1 0.31901 -1.151E-16
2 _Parm2 0.30153 1.8496E-16
3 _Parm3 0.20653 -2.468E-32
4 _Parm4 0.41695 -6.681E-16
5 _Parm5 0.34112 2.5981E-31
6 _Add1 105.12271 8.882E-34
7 _Add2 89.84359 4.4965E-34
8 _Add3 42.54028 6.5484E-18
9 _Add4 49.01931 7.4888E-19
10 _Add5 57.99673 6.3985E-34
Value of Objective Function = 0
Levenberg-Marquardt Optimization
Scaling Update of More (1978)
Parameter Estimates 10
Functions (Observations) 10
Optimization Start
Active Constraints 0 Objective Function 0
Max Abs Gradient Element 6.681129E-16 Radius 1
Optimization Results
Iterations 0 Function Calls
4
Jacobian Calls 1 Active Constraints
0
Objective Function 0 Max Abs Gradient
Element 6.681129E-16
Lambda 0 Actual Over Pred
Change 0
Radius 1
Convergence criterion (ABSGCONV=0.00001) satisfied.
Fit Summary
Modeling Info N Observations 200
N Variables 4
N Moments 10
N Parameters 10
N Active Constraints 0
Baseline Model Function Value 1.8576
Baseline Model Chi-Square 369.6536
Baseline Model Chi-Square DF 6
Pr > Baseline Model Chi-Square <.0001
Absolute Index Fit Function 0.0000
Chi-Square 0.0000
Chi-Square DF 0
Pr > Chi-Square .
Z-Test of Wilson & Hilferty .
Hoelter Critical N .
Root Mean Square Residual (RMSR) 0.0000
Standardized RMSR (SRMSR) 0.0000
Goodness of Fit Index (GFI) 1.0000
Parsimony Index Adjusted GFI (AGFI) .
Parsimonious GFI 0.0000
RMSEA Estimate .
Probability of Close Fit .
ECVI Estimate 0.1031
ECVI Lower 90% Confidence Limit .
ECVI Upper 90% Confidence Limit .
Akaike Information Criterion 20.0000
Bozdogan CAIC 62.9832
Schwarz Bayesian Criterion 52.9832
McDonald Centrality 1.0000
Incremental Index Bentler Comparative Fit Index 1.0000
Bentler-Bonett NFI 1.0000
Bentler-Bonett Non-normed Index .
Bollen Normed Index Rho1 .
Bollen Non-normed Index Delta2 1.0000
James et al. Parsimonious NFI 0.0000
PATH List
Standard
----------Path---------- Parameter Estimate Error t Value
SCIENCE <--- MATH _Parm1 0.31901 0.07610 4.19224
SCIENCE <--- READ _Parm2 0.30153 0.06816 4.42376
SCIENCE <--- WRITE _Parm3 0.20653 0.07023 2.94075
MATH <--- READ _Parm4 0.41695 0.05620 7.41912
MATH <--- WRITE _Parm5 0.34112 0.06079 5.61144
Variance Parameters
Variance Standard
Type Variable Parameter Estimate Error t Value
Exogenous READ _Add1 105.12271 10.53865 9.97497
WRITE _Add2 89.84359 9.00690 9.97497
Error MATH _Add3 42.54028 4.26470 9.97497
SCIENCE _Add4 49.01931 4.91423 9.97497
Covariances Among Exogenous Variables
Standard
Var1 Var2 Parameter Estimate Error t Value
WRITE READ _Add5 57.99673 8.02265 7.22912
Squared Multiple Correlations
Error Total
Variable Variance Variance R-Square
MATH 42.54028 87.76781 0.5153
SCIENCE 49.01931 98.02764 0.4999
Stability Coefficient of Reciprocal Causation = 0
Stability Coefficient < 1
Total and Indirect Effects Converge
Effects on SCIENCE
Effect / Std Error / t Value / p Value
Total Direct Indirect
READ 0.4345 0.3015 0.1330
0.0629 0.0682 0.0364
6.9046 4.4238 3.6499
<.0001 <.0001 0.000262
WRITE 0.3153 0.2065 0.1088
0.0681 0.0702 0.0324
4.6323 2.9407 3.3585
<.0001 0.003274 0.000784
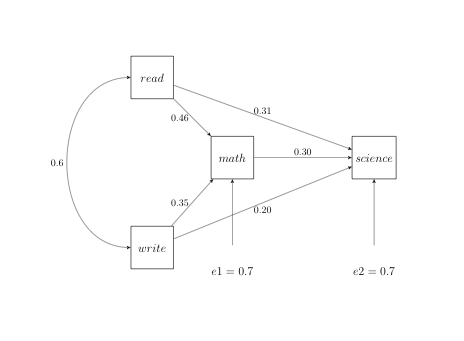
Standardized Results for PATH List
Standard
----------Path---------- Parameter Estimate Error t Value
SCIENCE <--- MATH _Parm1 0.30185 0.07073 4.26791
SCIENCE <--- READ _Parm2 0.31225 0.06919 4.51278
SCIENCE <--- WRITE _Parm3 0.19772 0.06676 2.96177
MATH <--- READ _Parm4 0.45631 0.05793 7.87688
MATH <--- WRITE _Parm5 0.34513 0.05977 5.77390
Standardized Results for Variance Parameters
Variance Standard
Type Variable Parameter Estimate Error t Value
Exogenous READ _Add1 1.00000
WRITE _Add2 1.00000
Error MATH _Add3 0.48469 0.04933 9.82568
SCIENCE _Add4 0.50006 0.05013 9.97553
Standardized Results for Covariances Among Exogenous Variables
Standard
Var1 Var2 Parameter Estimate Error t Value
WRITE READ _Add5 0.59678 0.04564 13.07520
Standardized Effects on SCIENCE
Effect / Std Error / tValue / pValue
Total Direct Indirect
READ 0.4500 0.3123 0.1377
0.0613 0.0692 0.0369
7.3450 4.5128 3.7366
<.0001 <.0001 0.000186
WRITE 0.3019 0.1977 0.1042
0.0637 0.0668 0.0305
4.7392 2.9618 3.4152
<.0001 0.003059 0.000637
We will focus our attention on the bolded parts of the output above which include the standardized results for path list, standardized results for variance parameters and the standardized effects on science. We will use the standardized estimates as our path coefficients and the square root of the variance estimates for the error. The error values are sqrt(0.48469) = .69619681 (approx = 0.7) for math and sqrt(0.50006) = .70714921 (approx = 0.7) for science. Now we can add the path coefficients and errors to the path diagram as shown below.
The proc calis also provides estimates of the direct, indirect and total effect for the two exogenous variables because we included the effpart substatement in our model. From these results we see that the indirect effect of read is about one third that of the direct effect. While for write the indirect effect is a bit more than half the size of the direct effect. For this example, the estimates for all of the direct and indirect effects were statistically significant. This is not necessarily a very common occurrence.