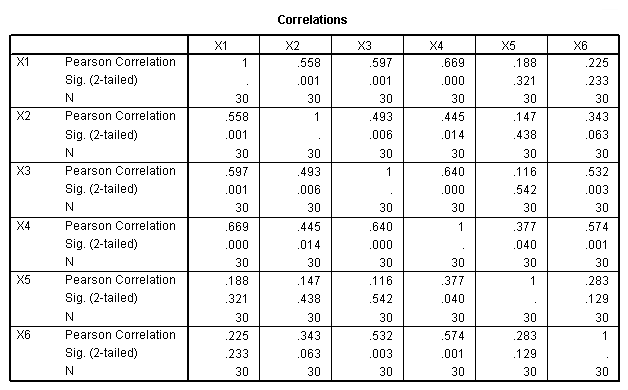
Table 11.1, page 295. Correlation Matrix for the Supervision Performance Data in Table 3.3.
get file 'd:p054.sav'. correlation variables = x1 x2 x3 x4 x5 x6.
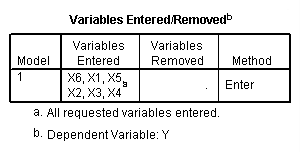
VIF, middle of page 295.
regression /statistics tol /dependent = y /method enter = x1 x2 x3 x4 x5 x6.
Eigenvalues, bottom of page 295.
factor variables = x1 x2 x3 x4 x5 x6 /criteria factors (6) /rotation norotate /method = correlation.
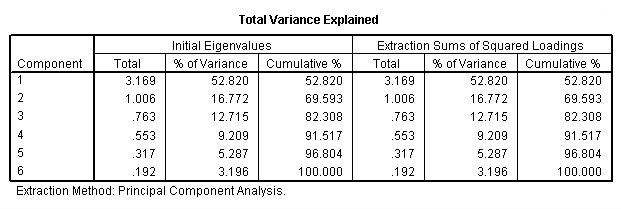
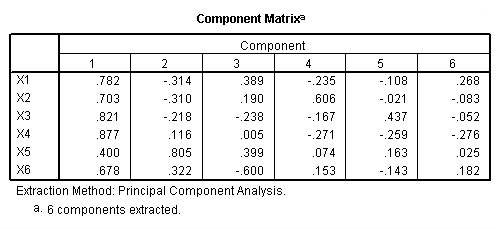
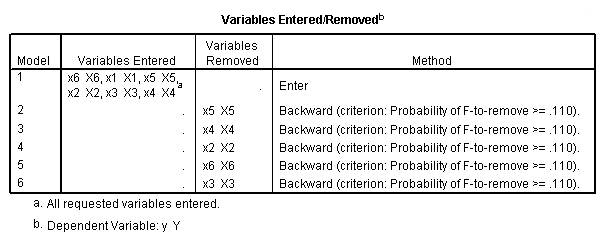
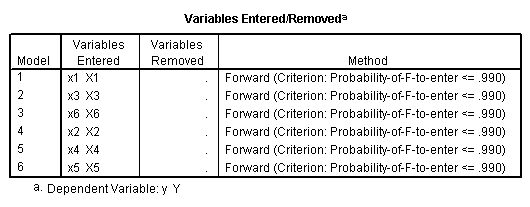
Table 11.2, page 296. Variables selected by the Forward Selection Method.
NOTE: The probability (p-value) for entering was set at .99 so that all the
variables will be entered into the model. The reason is that we are mainly
interested in the order in which they entered the model.
regression /statistics = selection coef outs r anova /criteria = pin(.99) pout(.1) /dependent = y /method = forward x1 x2 x3 x4 x5 x6.
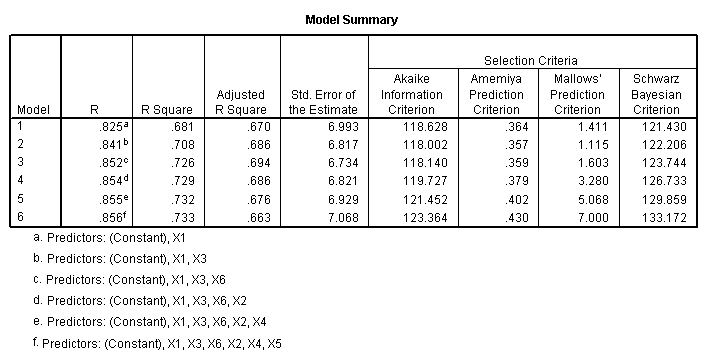
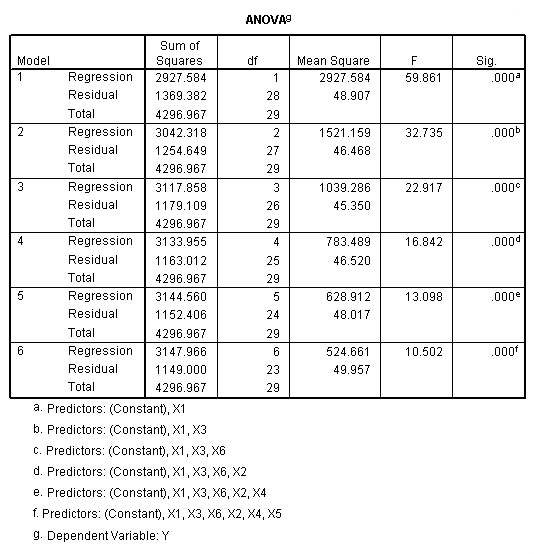
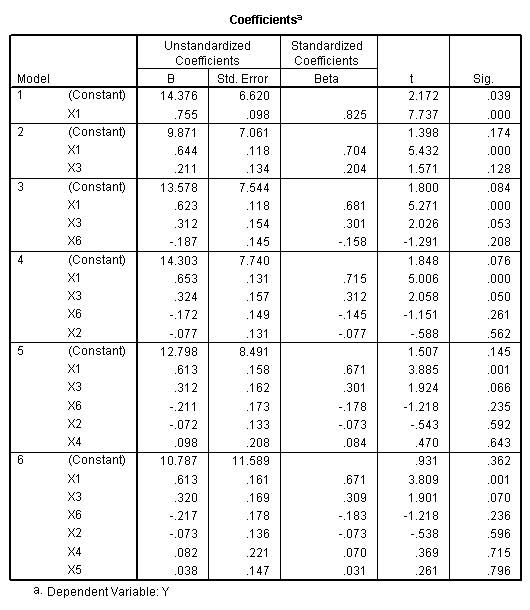
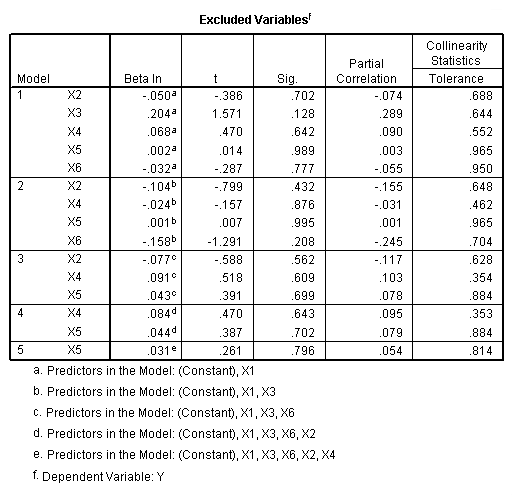
Regression Equation, page 296.
NOTE: The probability to remove, pout(.33) corresponds to a t-value of 1.0.
regression /statistics = coef /criteria = pin(.1) pout(.33) /dependent = y /method = backward x1 x2 x3 x4 x5 x6.
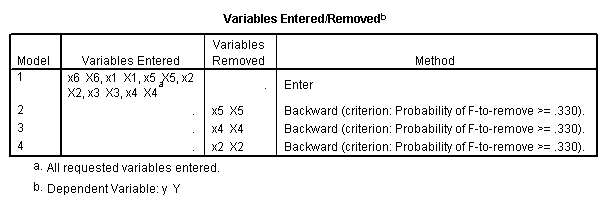
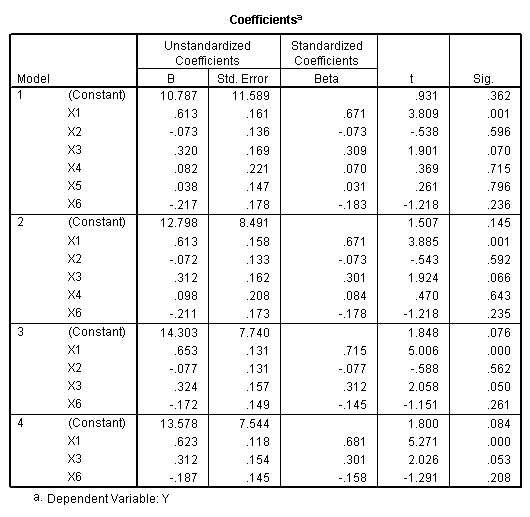
Table 11.3, page 297. Variables selected by the Backward Elimination Method.
NOTE: The probability (p-value) for removal was set at .01 so that all the
variables will be entered into the model.
regression /statistics = selection coef outs r anova /criteria = pin(.1) pout(.01) /dependent = y /method = backward x1 x2 x3 x4 x5 x6.
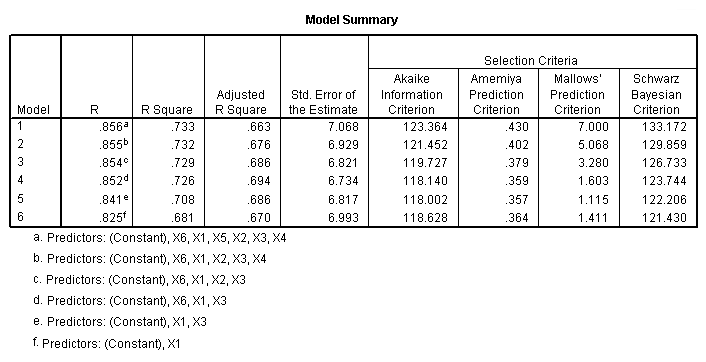
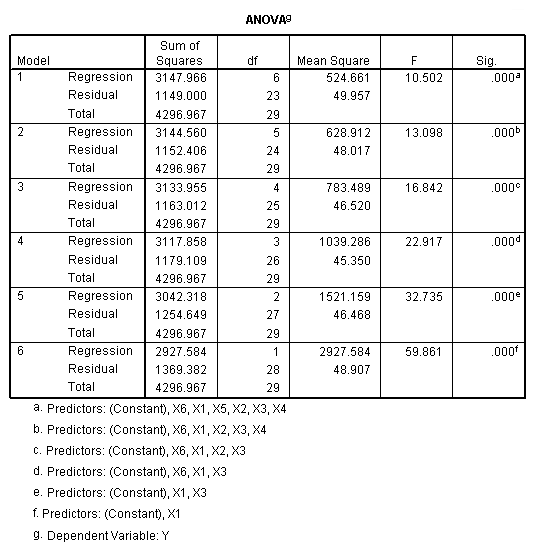
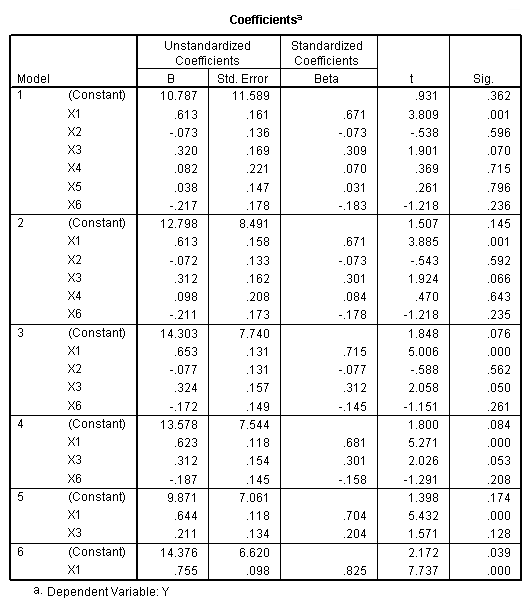
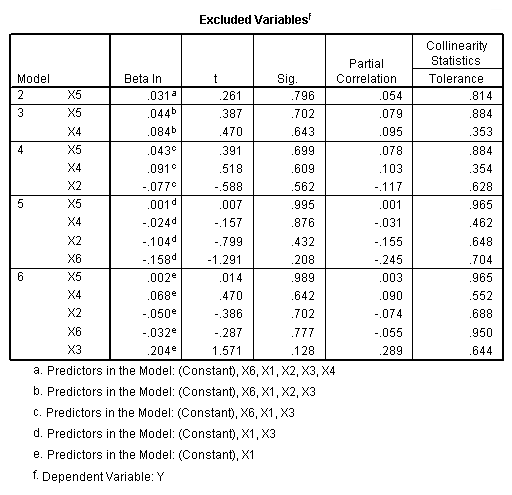
Table 11.4-11.5 page 297and Figure 11.1 page 298.
NOTE: SPSS does not have the best subset option.
Table 11.7, page 301. First Part of the Homicide Data.
get file 'd:p301.sav'. list variables year to clear.
year ftp unemp m lic gr clear
1961 260.35 11.00 455.50 178.15 215.98 93.40
1962 269.80 7.00 480.20 156.41 180.48 88.50
1963 272.04 5.20 506.10 198.02 209.57 94.40
1964 272.96 4.30 535.80 222.10 231.67 92.00
1965 272.51 3.50 576.00 301.92 297.65 91.00
1966 261.34 3.20 601.70 391.22 367.62 87.40
1967 268.89 4.10 577.30 665.56 616.54 88.30
1968 295.99 3.90 596.90 1131.21 1029.75 86.10
1969 319.87 3.60 613.50 837.80 786.23 79.00
1970 341.43 7.10 569.30 794.90 713.77 73.90
1971 356.59 8.40 548.80 817.74 750.43 63.40
1972 376.69 7.70 563.40 583.17 1027.38 62.50
1973 390.19 6.30 609.30 709.59 666.50 58.90
Number of cases read: 13 Number of cases listed: 13
Table 11.8, page 301. Second Part of the Homicide Data.
list variables year w to h.
year w nman g he we h
1961 558724 538.10 133.90 2.98 117.18 8.60
1962 538584 547.60 137.60 3.09 134.02 8.90
1963 519171 562.80 143.60 3.23 141.68 8.52
1964 500457 591.00 150.30 3.33 147.98 8.89
1965 482418 626.10 164.30 3.46 159.85 13.07
1966 465029 659.80 179.50 3.60 157.19 14.57
1967 448267 686.20 187.50 3.73 155.29 21.36
1968 432109 699.60 195.40 2.91 131.75 28.03
1969 416533 729.90 210.30 4.25 178.74 31.49
1970 401518 757.80 223.80 4.47 178.30 37.39
1971 398046 755.30 227.70 5.04 209.54 46.26
1972 373095 787.00 230.90 5.47 240.05 47.24
1973 359647 819.80 230.20 5.76 258.05 52.33
Number of cases read: 13 Number of cases listed: 13
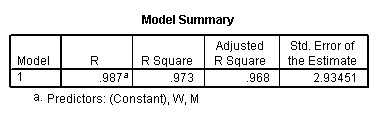
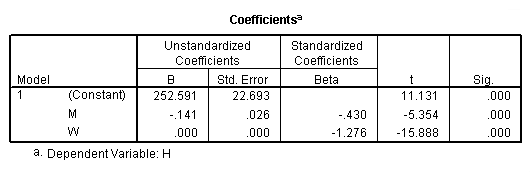
Table 11.9, page 301. The OLS Results From Fitting Model (11.8).
regression /statistics tol coef r /dependent = h /method enter = g m w.
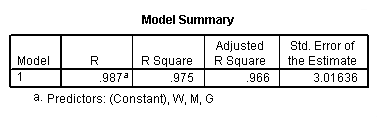
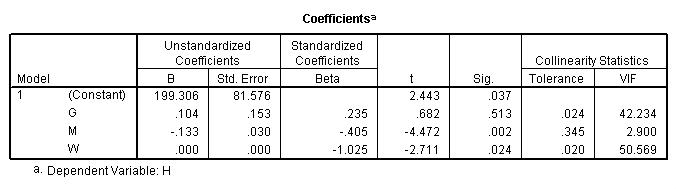
Table 11.10, page 302.
Model A.
regression /statistics coef r /dependent = h /method enter = g.
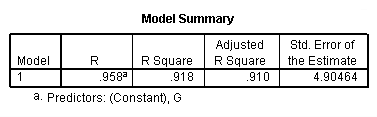
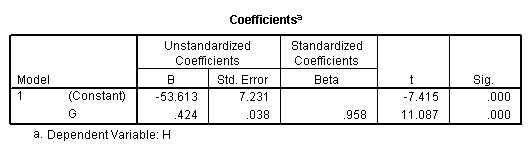
Model B.
regression /statistics coef r /dependent = h /method enter = m.
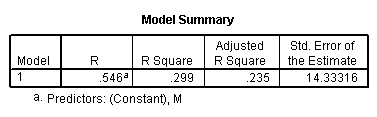
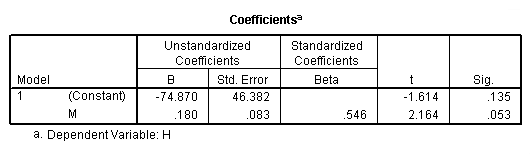
Model C.
regression /statistics coef r /dependent = h /method enter = w.
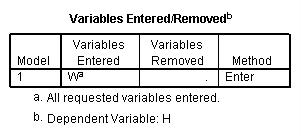
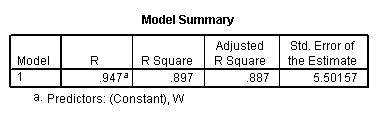
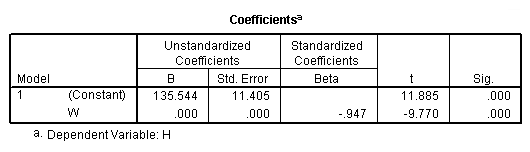
Model D.
regression /statistics coef r /dependent = h /method enter = g m.
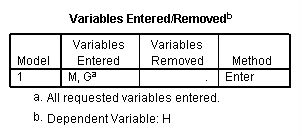
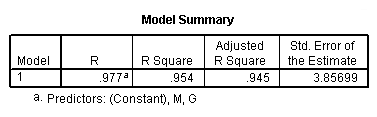
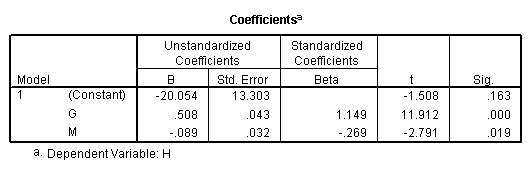
Model E.
regression /statistics coef r /dependent = h /method enter = g w.
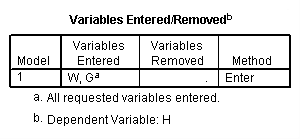
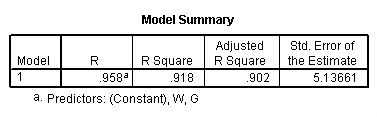
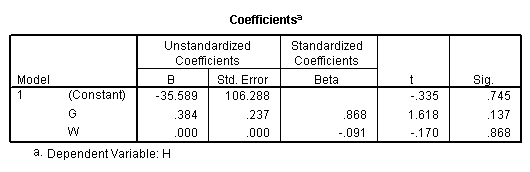
Model F.
regression /statistics coef r /dependent = h /method enter = g m w.
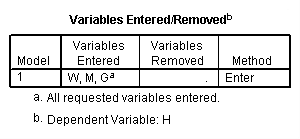
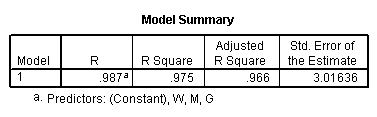
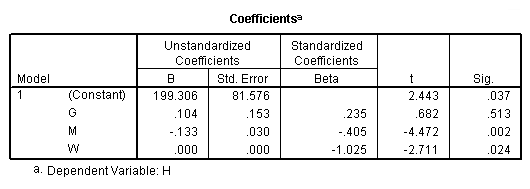
Model G.
regression /statistics coef r /dependent = h /method enter = m w.