use https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/stat/stata/examples/methods_matter/chapter7/sfa
Descriptive statistics for the variable wattack. Notice the floor effect which cannot be resolved by a straightforward transformation. (Note these analyses are not shown in the text.)
sum wattack, detail
word attack posttest
-------------------------------------------------------------
Percentiles Smallest
1% 440 440
5% 440 440
10% 449 440 Obs 2334
25% 466 440 Sum of Wgt. 2334
50% 479 Mean 478.5193
Largest Std. Dev. 19.87872
75% 492 537
90% 503 537 Variance 395.1636
95% 509 545 Skewness -.165475
99% 525 545 Kurtosis 2.801111
graph box wattack, medtype(line) ytitle(Word Attack Scores) ysize(3) xsize(2)
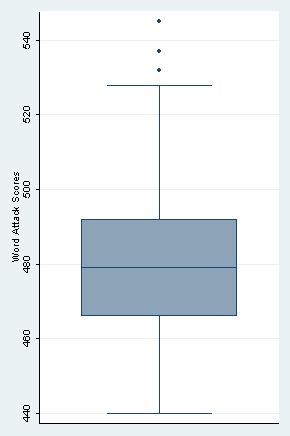
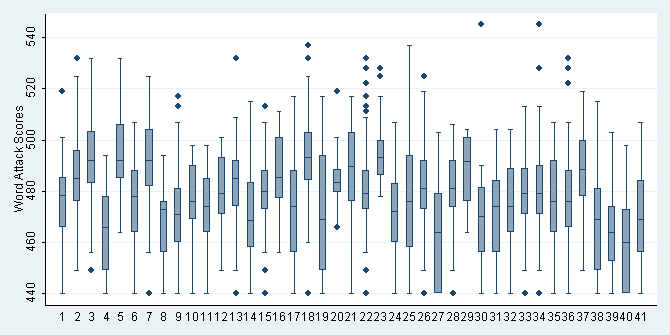
Descriptive analyses of wattack by school (schid). Note the floor effect is present in most schools. (Not shown in text.)
table schid, contents(mean wattack sd wattack min wattack max wattack freq)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
school id | mean(watt~k) sd(wattack) min(wattack) max(wattack) Freq.
----------+---------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 475.731 16.15988 440 519 52
2 | 486.603 15.31063 449 532 116
3 | 491.368 16.8469 449 532 68
4 | 462.912 16.55179 440 494 34
5 | 495.085 14.96783 464 532 47
6 | 475.115 18.07763 440 507 87
7 | 491.53 16.19119 440 525 83
8 | 467.5 13.9412 440 494 22
9 | 471.105 17.6963 440 517 95
10 | 474.556 19.07744 440 498 27
11 | 472.186 16.68797 440 498 43
12 | 478.963 13.21852 449 501 27
13 | 483.871 14.56414 440 532 62
14 | 469.889 17.18767 440 515 36
15 | 479.556 15.97128 440 513 54
16 | 486.75 14.86967 456 511 36
17 | 472.951 22.71998 440 517 41
18 | 492.596 17.52095 440 537 109
19 | 468.739 23.85604 440 517 23
20 | 484.75 11.13494 466 519 20
21 | 487.231 19.07008 440 517 134
22 | 480.274 18.01826 440 532 106
23 | 495.333 12.11611 478 528 36
24 | 470.771 17.15045 440 507 48
25 | 476.019 23.51344 440 537 52
26 | 480.97 18.02645 440 525 66
27 | 462.951 19.46015 440 503 41
28 | 480.839 15.78236 440 506 56
29 | 488.1 15.19832 464 504 10
30 | 469.625 22.41857 440 545 24
31 | 471.525 17.96627 440 504 61
32 | 474.724 17.77224 440 504 58
33 | 478.878 19.19921 440 513 41
34 | 479.418 19.18507 440 545 79
35 | 474.421 18.73494 440 507 57
36 | 476.929 20.63214 440 532 85
37 | 487.19 16.92756 449 519 58
38 | 468.189 21.31749 440 515 37
39 | 464.361 16.32553 440 503 36
40 | 459.252 16.97395 440 498 107
41 | 468.933 17.35362 440 507 60
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
graph box wattack, medtype(line) over(schid) ytitle(Word Attack Scores) ysize(2) xsize(4)
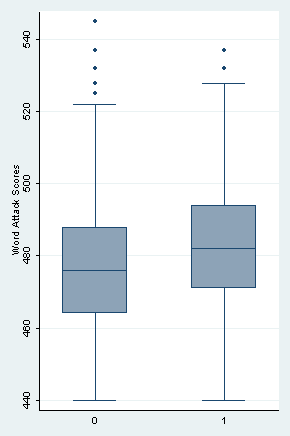
Descriptive analyses of wattack by experimental condition (sfa). (Not shown in text.)
bysort sfa: sum wattack, detail
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-> sfa = 0
word attack posttest
-------------------------------------------------------------
Percentiles Smallest
1% 440 440
5% 440 440
10% 440 440 Obs 1118
25% 464 440 Sum of Wgt. 1118
50% 476 Mean 474.8247
Largest Std. Dev. 20.05239
75% 488 532
90% 500 537 Variance 402.0982
95% 506 545 Skewness -.0207681
99% 525 545 Kurtosis 2.808253
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-> sfa = 1
word attack posttest
-------------------------------------------------------------
Percentiles Smallest
1% 440 440
5% 440 440
10% 456 440 Obs 1216
25% 471 440 Sum of Wgt. 1216
50% 482 Mean 481.9161
Largest Std. Dev. 19.10511
75% 494 532
90% 506 532 Variance 365.0053
95% 511 532 Skewness -.280702
99% 522 537 Kurtosis 2.936778
graph box wattack, medtype(line) over(sfa) ytitle(Word Attack Scores) ysize(3) xsize(2)
Model #1 from Table 7.1 on page 114.
xtreg wattack, i(schid)
Random-effects GLS regression Number of obs = 2334
Group variable: schid Number of groups = 41
R-sq: within = 0.0000 Obs per group: min = 10
between = 0.0000 avg = 56.9
overall = 0.0000 max = 134
Random effects u_i ~ Gaussian Wald chi2(0) = .
corr(u_i, X) = 0 (assumed) Prob > chi2 = .
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
wattack | Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
_cons | 477.5356 1.447118 329.99 0.000 474.6994 480.3719
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
sigma_u | 8.8705267
sigma_e | 17.725757
rho | .20027618 (fraction of variance due to u_i)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* variance of sigma u
display e(sigma_u)^2
78.686244
* variance of sigma e
display e(sigma_e)^2
314.20244
Model #2 from Table 7.1 on page 114.
xtreg wattack sfa, i(schid)
Random-effects GLS regression Number of obs = 2334
Group variable: schid Number of groups = 41
R-sq: within = 0.0000 Obs per group: min = 10
between = 0.0486 avg = 56.9
overall = 0.0318 max = 134
Random effects u_i ~ Gaussian Wald chi2(1) = 2.33
corr(u_i, X) = 0 (assumed) Prob > chi2 = 0.1271
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
wattack | Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
sfa | 4.362971 2.859467 1.53 0.127 -1.241483 9.967424
_cons | 475.3036 2.045759 232.34 0.000 471.294 479.3132
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
sigma_u | 8.7525004
sigma_e | 17.725757
rho | .19601985 (fraction of variance due to u_i)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* variance sigma u
display e(sigma_u)^2
76.606263
* variance sigma e
display e(sigma_e)^2
314.20244
Model #3 from Table 7.1 on page 114. The variable sch_ppvt is the within-school average of ppvt based on the full sample, rather than the subsample analyzed here, see footnote 15 on page 127.
xtreg wattack sfa sch_ppvt, i(schid)
Random-effects GLS regression Number of obs = 2334
Group variable: schid Number of groups = 41
R-sq: within = 0.0000 Obs per group: min = 10
between = 0.3820 avg = 56.9
overall = 0.0914 max = 134
Random effects u_i ~ Gaussian Wald chi2(2) = 23.58
corr(u_i, X) = 0 (assumed) Prob > chi2 = 0.0000
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
wattack | Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
sfa | 3.572224 2.33971 1.53 0.127 -1.013523 8.15797
sch_ppvt | .6228176 .139824 4.45 0.000 .3487675 .8968676
_cons | 419.8154 12.55807 33.43 0.000 395.202 444.4287
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
sigma_u | 6.9693079
sigma_e | 17.725757
rho | .13388857 (fraction of variance due to u_i)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* variance sigma u
display e(sigma_u)^2
48.571253
* variance sigma e
display e(sigma_e)^2
314.20244
Model #3 using the within-school averages of prior ppvt score (new variable schavgppvt) from the analytic subsample instead of sch_ppvt. (Not shown in text, this analysis is mentioned in footnote 15 on page 127.)
bysort schid: egen schavgppvt = mean(ppvt)
xtreg wattack sfa schavgppvt, i(schid)
Random-effects GLS regression Number of obs = 2334
Group variable: schid Number of groups = 41
R-sq: within = 0.0000 Obs per group: min = 10
between = 0.4003 avg = 56.9
overall = 0.0977 max = 134
Random effects u_i ~ Gaussian Wald chi2(2) = 25.57
corr(u_i, X) = 0 (assumed) Prob > chi2 = 0.0000
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
wattack | Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
sfa | 3.218344 2.311869 1.39 0.164 -1.312837 7.749524
schavgppvt | .6023257 .1293094 4.66 0.000 .348884 .8557674
_cons | 421.6086 11.6332 36.24 0.000 398.8079 444.4092
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
sigma_u | 6.8490081
sigma_e | 17.725757
rho | .12990151 (fraction of variance due to u_i)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following models show various ways of controlling for individual- and school-level ppvt. None of the models shown below are displayed in the text.
Controlling for individual-level ppvt, deviated from the grand mean (new variable ppvt_devgm).
sum ppvt
Variable | Obs Mean Std. Dev. Min Max
-------------+--------------------------------------------------------
ppvt | 2334 90.4006 15.00082 40 144
gen ppvt_devgm = ppvt-90.4006
xtreg wattack sfa ppvt_devgm, i(schid)
Random-effects GLS regression Number of obs = 2334
Group variable: schid Number of groups = 41
R-sq: within = 0.1101 Obs per group: min = 10
between = 0.3960 avg = 56.9
overall = 0.1820 max = 134
Random effects u_i ~ Gaussian Wald chi2(2) = 308.21
corr(u_i, X) = 0 (assumed) Prob > chi2 = 0.0000
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
wattack | Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
sfa | 3.440921 2.297268 1.50 0.134 -1.061642 7.943485
ppvt_devgm | .4851754 .0278075 17.45 0.000 .4306737 .5396771
_cons | 475.9076 1.642957 289.67 0.000 472.6875 479.1278
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
sigma_u | 6.9082397
sigma_e | 16.725172
rho | .14574142 (fraction of variance due to u_i)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Controlling for individual-level ppvt by including deviations of individual scores from school-average scores (new variable ppvt_devsm) and school-average scores from the grand mean (new variable schavgppvt_devgm).
gen ppvt_devsm = ppvt-schavgppvt
gen schavgppvt_devgm = schavgppvt-90.4006
xtreg wattack sfa ppvt_devsm schavgppvt_devgm, i(schid)
Random-effects GLS regression Number of obs = 2334
Group variable: schid Number of groups = 41
R-sq: within = 0.1101 Obs per group: min = 10
between = 0.4004 avg = 56.9
overall = 0.1835 max = 134
Random effects u_i ~ Gaussian Wald chi2(3) = 308.73
corr(u_i, X) = 0 (assumed) Prob > chi2 = 0.0000
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
wattack | Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
sfa | 3.187396 2.331659 1.37 0.172 -1.382572 7.757363
ppvt_devsm | .4794657 .0284703 16.84 0.000 .4236648 .5352666
schavgppvt~m | .6030759 .1303864 4.63 0.000 .3475233 .8586285
_cons | 476.0634 1.664848 285.95 0.000 472.8003 479.3264
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
sigma_u | 6.9726021
sigma_e | 16.725172
rho | .14806577 (fraction of variance due to u_i)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Controlling for school-average ppvt deviated from the grand mean (schavgppvt_devgm).
xtreg wattack sfa schavgppvt_devgm, i(schid)
Random-effects GLS regression Number of obs = 2334
Group variable: schid Number of groups = 41
R-sq: within = 0.0000 Obs per group: min = 10
between = 0.4003 avg = 56.9
overall = 0.0977 max = 134
Random effects u_i ~ Gaussian Wald chi2(2) = 25.57
corr(u_i, X) = 0 (assumed) Prob > chi2 = 0.0000
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
wattack | Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
sfa | 3.218344 2.311869 1.39 0.164 -1.312837 7.749524
schavgppvt~m | .6023257 .1293094 4.66 0.000 .348884 .8557674
_cons | 476.0592 1.650323 288.46 0.000 472.8246 479.2937
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
sigma_u | 6.8490081
sigma_e | 17.725757
rho | .12990151 (fraction of variance due to u_i)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
