This page is just an extension of How can I do moderated mediation in Stata? to include a categorical moderator variables. We will call that page modmed. If you are unfamiliar with moderated mediation you should review the modmed FAQ page before continuing on with this page.
We will to use the same data and the same abbreviated variable names as were used on the modmed page. The model is not of substantive interest, it is merely used to show the steps involved in the analysis.
use https://stats.idre.ucla.edu/stat/data/hsbdemo, clear rename science y /* dependent variable */ rename math x /* independent variable */ rename read m /* mediator variable */ rename female w /* moderator variable with 2 levels */ rename socst cv /* continuous covariate */
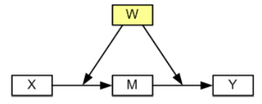
The modmed page presented five different models for moderated mediation. This page will cover models 5, 2 and 3, to illustrate the use of categorical moderators. The diagram for model 5 looks like this:
Model 5
First pass using sem
The trick to using sem for moderated mediation with a categorical moderator is to do a multiple group analysis using the group option. Please note, there are no explicit interactions in the model. The interactions are implicit in the multiple group analysis itself. Here is our first try.
sem (m <- x cv)(y <- m x cv), group(w)
Endogenous variables
Observed: m y
Exogenous variables
Observed: x cv
Fitting target model:
Iteration 0: log likelihood = -2792.7769
Iteration 1: log likelihood = -2792.7769
Structural equation model Number of obs = 200
Grouping variable = w Number of groups = 2
Estimation method = ml
Log likelihood = -2792.7769
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| OIM
| Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
Structural |
m <- |
x |
male | .4461113 .09393 4.75 0.000 .262012 .6302107
female | .5523602 .0843711 6.55 0.000 .3869959 .7177244
cv |
male | .3687237 .0800976 4.60 0.000 .2117353 .525712
female | .3444715 .0754397 4.57 0.000 .1966124 .4923306
_cons |
male | 10.10814 4.69041 2.16 0.031 .9151099 19.30118
female | 4.564765 3.855135 1.18 0.236 -2.991162 12.12069
-----------+----------------------------------------------------------------
y <- |
m |
male | .4504614 .1045896 4.31 0.000 .2454696 .6554532
female | .211106 .0977165 2.16 0.031 .0195853 .4026267
x |
male | .3523138 .1046885 3.37 0.001 .1471281 .5574996
female | .452633 .1015976 4.46 0.000 .2535052 .6517607
cv |
male | .0497414 .0887335 0.56 0.575 -.1241731 .223656
female | .0458989 .0840018 0.55 0.585 -.1187416 .2105395
_cons |
male | 8.206073 4.797652 1.71 0.087 -1.197152 17.6093
female | 13.63157 3.958183 3.44 0.001 5.873677 21.38947
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
Variance |
e.m |
male | 55.76584 8.267278 41.704 74.56907
female | 41.59327 5.634104 31.89494 54.24058
e.y |
male | 55.51193 8.229635 41.51411 74.22955
female | 43.28974 5.863902 33.19584 56.4529
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
LR test of model vs. saturated: chi2(0) = 0.00, Prob > chi2 = .
This isn’t too bad. We are getting separate male and female coefficients for both x and m. However, we are also getting separate coefficients for cv and separate residual variances in each equations. In a traditional moderated mediation model these values are not part of the interaction. So, we will need to constrain the coefficients for cv and residual variances to be equal in both equations. Here is how to do that.
Model 5 constraining the covariate to be equal across groups
Equations that begin with 0: refer to the male group and equations that begin with 1: refer to the female group. To constrain values use a ‘@’ and a name. Terms with the same name will be constrained to be equal. For example, the term cv@c1 will be constrained to be equal in both equations.
sem (0: m <- x cv@c1)(0: y <- m x cv@c2) ///
(1: m <- x cv@c1)(1: y <- m x cv@c2), group(w) ///
variance(0: e.m@v1 e.y@v2) ///
variance(1: e.m@v1 e.y@v2)
Endogenous variables
Observed: m y
Exogenous variables
Observed: x cv
Fitting target model:
Iteration 0: log likelihood = -2795.5195
Iteration 1: log likelihood = -2794.6484
Iteration 2: log likelihood = -2794.6438
Iteration 3: log likelihood = -2794.6438
Structural equation model Number of obs = 200
Grouping variable = w Number of groups = 2
Estimation method = ml
Log likelihood = -2794.6438
( 1) [m]0bn.w#c.cv - [m]1.w#c.cv = 0
( 2) [y]0bn.w#c.cv - [y]1.w#c.cv = 0
( 3) [var(e.m)]0bn.w - [var(e.m)]1.w = 0
( 4) [var(e.y)]0bn.w - [var(e.y)]1.w = 0
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| OIM
| Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
Structural |
m <- |
x |
male | .4525824 .0821032 5.51 0.000 .291663 .6135017
female | .5435942 .0815035 6.67 0.000 .3838503 .7033381
cv |
[*] | .3576463 .0548017 6.53 0.000 .2502369 .4650556
_cons |
male | 10.33924 4.225914 2.45 0.014 2.056605 18.62188
female | 4.326879 4.000737 1.08 0.279 -3.514422 12.16818
-----------+----------------------------------------------------------------
y <- |
m |
male | .4513773 .0937037 4.82 0.000 .2677214 .6350331
female | .2101483 .0992473 2.12 0.034 .0156271 .4046694
x |
male | .3527524 .0972145 3.63 0.000 .1622155 .5432893
female | .4520144 .1061237 4.26 0.000 .2440157 .6600131
cv |
[*] | .0479536 .0608685 0.79 0.431 -.0713466 .1672537
_cons |
male | 8.227069 4.450954 1.85 0.065 -.4966419 16.95078
female | 13.6048 4.117905 3.30 0.001 5.533856 21.67575
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
Variance |
e.m |
[*] | 48.05346 4.805346 39.50068 58.45812
e.y |
[*] | 48.85108 4.885108 40.15633 59.42843
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note: [*] identifies parameter estimates constrained to be equal across
groups.
LR test of model vs. saturated: chi2(4) = 3.73, Prob > chi2 = 0.4432
Now we can use the estat teffects to calculate the indirect effects for both males and females.
estat teffects
Direct effects
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| OIM
| Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
Structural |
m <- |
x |
male | .4525824 .0821032 5.51 0.000 .291663 .6135017
female | .5435942 .0815035 6.67 0.000 .3838503 .7033381
cv |
male | .3576463 .0548017 6.53 0.000 .2502369 .4650556
female | .3576463 .0548017 6.53 0.000 .2502369 .4650556
-----------+----------------------------------------------------------------
y <- |
m |
male | .4513773 .0937037 4.82 0.000 .2677214 .6350331
female | .2101483 .0992473 2.12 0.034 .0156271 .4046694
x |
male | .3527524 .0972145 3.63 0.000 .1622155 .5432893
female | .4520144 .1061237 4.26 0.000 .2440157 .6600131
cv |
male | .0479536 .0608685 0.79 0.431 -.0713466 .1672537
female | .0479536 .0608685 0.79 0.431 -.0713466 .1672537
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Indirect effects
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| OIM
| Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
Structural |
m <- |
x |
[*] | 0 (no path)
cv |
[*] | 0 (no path)
-----------+----------------------------------------------------------------
y <- |
m |
[*] | 0 (no path)
x |
male | .2042854 .0563196 3.63 0.000 .0939009 .3146699
female | .1142354 .0566038 2.02 0.044 .0032939 .2251768
cv |
male | .1614334 .0416532 3.88 0.000 .0797947 .2430722
female | .0751587 .037317 2.01 0.044 .0020188 .1482986
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note: [*] identifies parameter estimates constrained to be equal across
groups.
Total effects
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| OIM
| Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
Structural |
m <- |
x |
male | .4525824 .0821032 5.51 0.000 .291663 .6135017
female | .5435942 .0815035 6.67 0.000 .3838503 .7033381
cv |
male | .3576463 .0548017 6.53 0.000 .2502369 .4650556
female | .3576463 .0548017 6.53 0.000 .2502369 .4650556
-----------+----------------------------------------------------------------
y <- |
m |
male | .4513773 .0937037 4.82 0.000 .2677214 .6350331
female | .2101483 .0992473 2.12 0.034 .0156271 .4046694
x |
male | .5570378 .0914805 6.09 0.000 .3777393 .7363362
female | .5662498 .0857084 6.61 0.000 .3982643 .7342352
cv |
male | .209387 .0638934 3.28 0.001 .0841582 .3346158
female | .1231123 .0621467 1.98 0.048 .0013071 .2449176
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The indirect effect of x on y for males is .2042854 while for females it is .1142354.
Next we will look at Model 2.
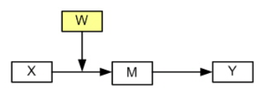
Model 2
Here is the diagram for Model 2.
For this model there is an interaction between w and x only in the mediator equation so we have to constrain the coefficient for the mediator to be equal in both equations in addition to the covariate and residuals.
sem (0: m <- x cv@c1)(0: y <- m@b1 x cv@c2) ///
(1: m <- x cv@c1)(1: y <- m@b1 x cv@c2), group(w) ///
variance(0: e.m@v1 e.y@v2) ///
variance(1: e.m@v1 e.y@v2)
Endogenous variables
Observed: m y
Exogenous variables
Observed: x cv
Fitting target model:
Iteration 0: log likelihood = -2880.2553
Iteration 1: log likelihood = -2814.5984
Iteration 2: log likelihood = -2797.118
Iteration 3: log likelihood = -2796.3599
Iteration 4: log likelihood = -2796.3547
Iteration 5: log likelihood = -2796.3547
Structural equation model Number of obs = 200
Grouping variable = w Number of groups = 2
Estimation method = ml
Log likelihood = -2796.3547
( 1) [y]0bn.w#c.m - [y]1.w#c.m = 0
( 2) [m]0bn.w#c.cv - [m]1.w#c.cv = 0
( 3) [y]0bn.w#c.cv - [y]1.w#c.cv = 0
( 4) [var(e.m)]0bn.w - [var(e.m)]1.w = 0
( 5) [var(e.y)]0bn.w - [var(e.y)]1.w = 0
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| OIM
| Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
Structural |
m <- |
x |
male | .4525824 .0821032 5.51 0.000 .291663 .6135017
female | .5435942 .0815035 6.67 0.000 .3838503 .7033381
cv |
[*] | .3576463 .0548017 6.53 0.000 .2502369 .4650557
_cons |
male | 10.33924 4.225914 2.45 0.014 2.056604 18.62188
female | 4.326879 4.000738 1.08 0.279 -3.514423 12.16818
-----------+----------------------------------------------------------------
y <- |
m |
[*] | .3384145 .0719076 4.71 0.000 .1974781 .4793508
x |
male | .4260495 .0896114 4.75 0.000 .2504144 .6016846
female | .3501396 .091638 3.82 0.000 .1705324 .5297469
cv |
[*] | .0503993 .0613771 0.82 0.412 -.0698976 .1706962
_cons |
male | 10.18685 4.361284 2.34 0.020 1.638888 18.73481
female | 12.17734 4.080339 2.98 0.003 4.180026 20.17466
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
Variance |
e.m |
[*] | 48.05346 4.805346 39.50068 58.45812
e.y |
[*] | 49.69406 4.969406 40.84927 60.45394
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note: [*] identifies parameter estimates constrained to be equal across
groups.
LR test of model vs. saturated: chi2(5) = 7.16, Prob > chi2 = 0.2093
estat teffects
Direct effects
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| OIM
| Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
Structural |
m <- |
x |
male | .4525824 .0821032 5.51 0.000 .291663 .6135017
female | .5435942 .0815035 6.67 0.000 .3838503 .7033381
cv |
male | .3576463 .0548017 6.53 0.000 .2502369 .4650557
female | .3576463 .0548017 6.53 0.000 .2502369 .4650557
-----------+----------------------------------------------------------------
y <- |
m |
male | .3384145 .0719076 4.71 0.000 .1974781 .4793508
female | .3384145 .0719076 4.71 0.000 .1974781 .4793508
x |
male | .4260495 .0896114 4.75 0.000 .2504144 .6016846
female | .3501396 .091638 3.82 0.000 .1705324 .5297469
cv |
male | .0503993 .0613771 0.82 0.412 -.0698976 .1706962
female | .0503993 .0613771 0.82 0.412 -.0698976 .1706962
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Indirect effects
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| OIM
| Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
Structural |
m <- |
x |
[*] | 0 (no path)
cv |
[*] | 0 (no path)
-----------+----------------------------------------------------------------
y <- |
m |
[*] | 0 (no path)
x |
male | .1531604 .0427916 3.58 0.000 .0692904 .2370304
female | .1839601 .0478402 3.85 0.000 .0901952 .2777251
cv |
male | .1210327 .031707 3.82 0.000 .0588882 .1831772
female | .1210327 .031707 3.82 0.000 .0588882 .1831772
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note: [*] identifies parameter estimates constrained to be equal across
groups.
Total effects
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| OIM
| Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
Structural |
m <- |
x |
male | .4525824 .0821032 5.51 0.000 .291663 .6135017
female | .5435942 .0815035 6.67 0.000 .3838503 .7033381
cv |
male | .3576463 .0548017 6.53 0.000 .2502369 .4650557
female | .3576463 .0548017 6.53 0.000 .2502369 .4650557
-----------+----------------------------------------------------------------
y <- |
m |
male | .3384145 .0719076 4.71 0.000 .1974781 .4793508
female | .3384145 .0719076 4.71 0.000 .1974781 .4793508
x |
male | .57921 .0879948 6.58 0.000 .4067433 .7516766
female | .5340998 .087352 6.11 0.000 .3628929 .7053066
cv |
male | .171432 .0587342 2.92 0.004 .0563151 .2865488
female | .171432 .0587342 2.92 0.004 .0563151 .2865488
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This time the indirect effect of x on y for males is .1531604 while for females it is .1839601.
Next up is Model 3.
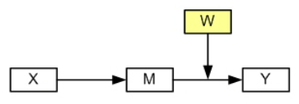
Model 3
Here is the diagram for Model 3.
For Model 3 the interaction term is only in the equation for the dependent variable, y. To compute the indirect effect we will need to constrain the coefficient for x in both equations along with cv and the residuals. In addition we will need to constrain the constant, _cons to be equal in both groups for the first equation.
sem (0: m <- x@b1 cv@c1 _cons@i1)(0: y <- m x@b2 cv@c2) ///
(1: m <- x@b1 cv@c1 _cons@i1)(1: y <- m x@b2 cv@c2), group(w) ///
variance(0: e.m@v1 e.y@v2) ///
variance(1: e.m@v1 e.y@v2)
Endogenous variables
Observed: m y
Exogenous variables
Observed: x cv
Fitting target model:
Iteration 0: log likelihood = -2809.2798
Iteration 1: log likelihood = -2797.463
Iteration 2: log likelihood = -2796.0327
Iteration 3: log likelihood = -2796.0196
Iteration 4: log likelihood = -2796.0196
Structural equation model Number of obs = 200
Grouping variable = w Number of groups = 2
Estimation method = ml
Log likelihood = -2796.0196
( 1) [m]0bn.w#c.x - [m]1.w#c.x = 0
( 2) [m]0bn.w#c.cv - [m]1.w#c.cv = 0
( 3) [y]0bn.w#c.x - [y]1.w#c.x = 0
( 4) [y]0bn.w#c.cv - [y]1.w#c.cv = 0
( 5) [var(e.m)]0bn.w - [var(e.m)]1.w = 0
( 6) [var(e.y)]0bn.w - [var(e.y)]1.w = 0
( 7) [m]0bn.w - [m]1.w = 0
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| OIM
| Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
Structural |
m <- |
x |
[*] | .5038419 .0628899 8.01 0.000 .3805799 .6271038
cv |
[*] | .35414 .05488 6.45 0.000 .2465771 .4617029
_cons |
[*] | 7.146537 3.017773 2.37 0.018 1.231809 13.06126
-----------+----------------------------------------------------------------
y <- |
m |
male | .425432 .0861437 4.94 0.000 .2565935 .5942706
female | .2444712 .0863545 2.83 0.005 .0752194 .4137229
x |
[*] | .3979248 .0727133 5.47 0.000 .2554093 .5404402
cv |
[*] | .0489704 .0609254 0.80 0.422 -.0704413 .168382
_cons |
male | 7.15329 4.182562 1.71 0.087 -1.04438 15.35096
female | 14.60934 3.86371 3.78 0.000 7.036603 22.18207
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
Variance |
e.m |
[*] | 48.6004 4.86004 39.95027 59.12348
e.y |
[*] | 48.97042 4.897041 40.25443 59.57361
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note: [*] identifies parameter estimates constrained to be equal across
groups.
LR test of model vs. saturated: chi2(7) = 6.49, Prob > chi2 = 0.4843
estat teffects
Direct effects
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| OIM
| Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
Structural |
m <- |
x |
male | .5038419 .0628899 8.01 0.000 .3805799 .6271038
female | .5038419 .0628899 8.01 0.000 .3805799 .6271038
cv |
male | .35414 .05488 6.45 0.000 .2465771 .4617029
female | .35414 .05488 6.45 0.000 .2465771 .4617029
-----------+----------------------------------------------------------------
y <- |
m |
male | .425432 .0861437 4.94 0.000 .2565935 .5942706
female | .2444712 .0863545 2.83 0.005 .0752194 .4137229
x |
male | .3979248 .0727133 5.47 0.000 .2554093 .5404402
female | .3979248 .0727133 5.47 0.000 .2554093 .5404402
cv |
male | .0489704 .0609254 0.80 0.422 -.0704413 .168382
female | .0489704 .0609254 0.80 0.422 -.0704413 .168382
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Indirect effects
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| OIM
| Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
Structural |
m <- |
x |
[*] | 0 (no path)
cv |
[*] | 0 (no path)
-----------+----------------------------------------------------------------
y <- |
m |
[*] | 0 (no path)
x |
male | .2143505 .0509868 4.20 0.000 .1144182 .3142827
female | .1231748 .0461456 2.67 0.008 .032731 .2136186
cv |
male | .1506625 .038416 3.92 0.000 .0753685 .2259565
female | .086577 .0333952 2.59 0.010 .0211236 .1520304
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note: [*] identifies parameter estimates constrained to be equal across
groups.
Total effects
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| OIM
| Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
Structural |
m <- |
x |
male | .5038419 .0628899 8.01 0.000 .3805799 .6271038
female | .5038419 .0628899 8.01 0.000 .3805799 .6271038
cv |
male | .35414 .05488 6.45 0.000 .2465771 .4617029
female | .35414 .05488 6.45 0.000 .2465771 .4617029
-----------+----------------------------------------------------------------
y <- |
m |
male | .425432 .0861437 4.94 0.000 .2565935 .5942706
female | .2444712 .0863545 2.83 0.005 .0752194 .4137229
x |
male | .6122752 .0745834 8.21 0.000 .4660944 .758456
female | .5210996 .0681111 7.65 0.000 .3876042 .654595
cv |
male | .1996329 .0622773 3.21 0.001 .0775716 .3216941
female | .1355474 .0595838 2.27 0.023 .0187652 .2523295
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This time the indirect effect of x on y for males is .2143505 while for females it is .1231748.