Note that unless otherwise noted, we used IGLS estimation.
In this chapter we will be using the following centered variables: GndC_verb is iq_verb centered around the grand mean; GrpM_verb contains the group means of iq_verb; GrpMC_verb contains the group means of GndC_verb. Furthermore, we will be creating the following centered variables: GrpC_size which is the group centered variable for groupsiz; GndC_ses is ses centered around the grand mean; verbXgsize which is the interaction of GndC_verb and GndC_gsize.
From chapter 4: creating the variables constant, GndC_verb and GrpMC_verb.
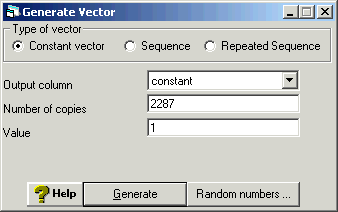
Creating the constant variable.
Data Manipulation
Names
This opens up a window listing all the variables in the dataset with the
number of non-missing observations, missing observation, max and min for
each variable. We just need to find out the total number of observations
in the dataset but this is a nice window to have open to keep an eye on
which variables have been corrected and do they look reasonable.
Generate Vector
For the output column choose an unused variable and rename it cons by
using ctrl+n which brings up a rename window. Then enter the total
number of observations in the data set for number of copies, in this
case n=2287. Finally, enter 1 for the value since this will be a constant
variable equal to 1.
Click generate in order to execute the command
Calculating the grand mean for iq_verb and then creating the variable gndc_verb which is centered around the grand mean.
Basic Statistics Averages and Correlations Choose iq_verb and click on calculate.
Calculate Choose an unused variable and rename it gndc_verb by using ctrl+n Enter "gndc_verb" = "iq_verb" - 11.834 and click on calculate.
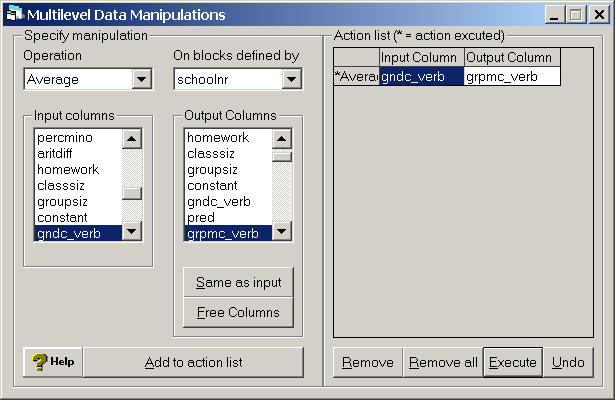
Creating the variable grpmc_verb which contains the group means of gndc_verb.
Data Manipulation
Multilevel Data Manipulation
in the input column choose gndc_verb, in the output column choose an unused variable and use ctrl+N
to rename it grpmc_verb then this will be the output variable
Click Add to action list which will make the input and output choices appear in the action list
on the right hand side
Click on Execute
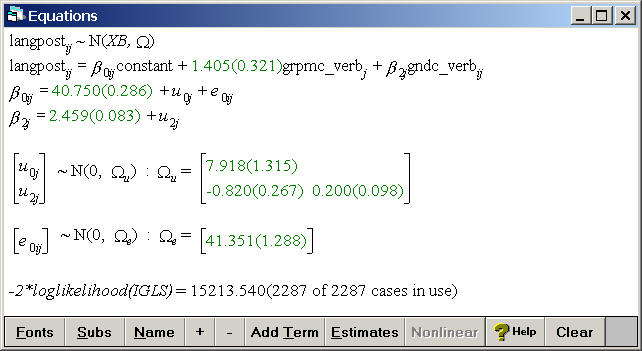
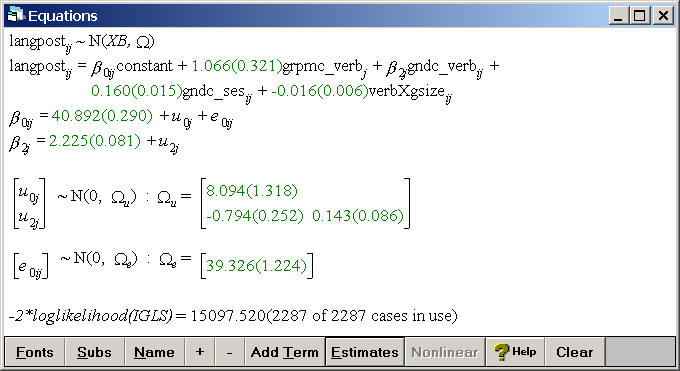
Table 5.1, p. 71.
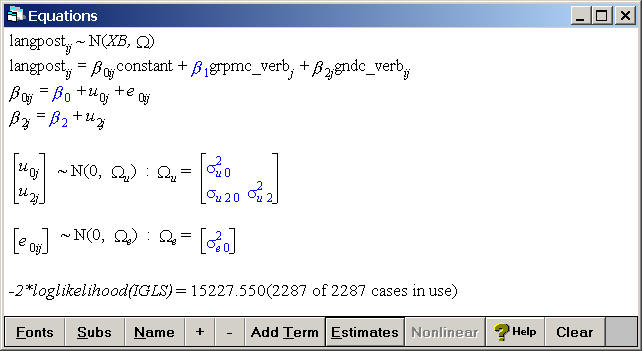
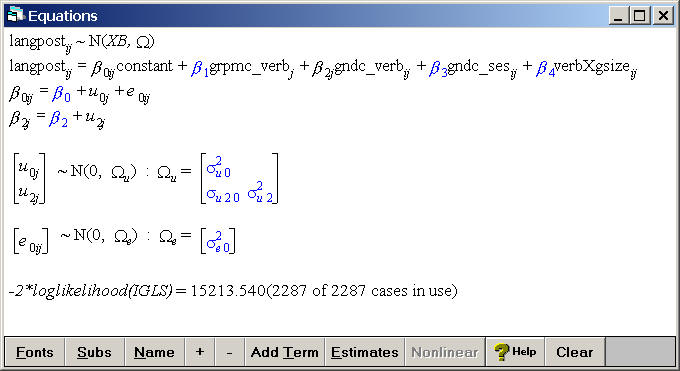
Random slope model including grpmc_verb as a fixed effect and gndc_verb as a both a random slope and as a fixed effect.
Model
Equations
Click on Y
Choose y: langpost, N levels: 2 - ij, level2(j): schoolnr, and
level1(i): pupilnr.
Click on the x0 variable
Choose the variable constant and select both schoolnr and pupilnr.
Add Term
Click on the x1 variable
Choose grpmc_verb as a fixed parameter
Add Term
Click on the x2 variable
Choose gndc_verb as a fixed parameter and as a random slope with variance
at the j(schoolnr) level
Click on the Start button located below the file menu and then click on estimates at the bottom of the equations window to make the estimates appear.
Generate the predicted values from the model in table 5.1 and storing them in the variable pred.
Model
Predictions
in the field called output from prediction to choose pred
Click on Name to see the names of the variables in the model
Click on constant, grpmc_verb and gndc_verb which will make all the
parameters in the model appear in black
Click on the level 1 error term to make it grey since we do not want to model this error term
Click on Calc to generate the predicted values and store them in the variable pred
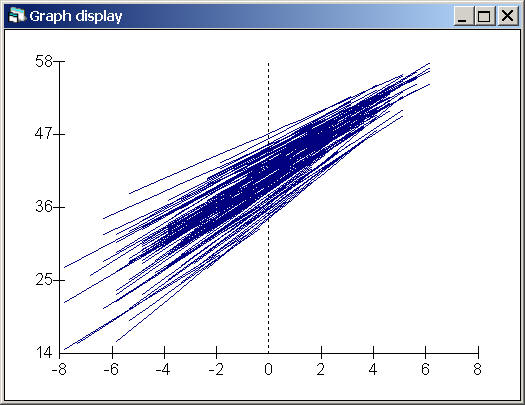
Fig. 5.2, p. 79.
This graph shows the regression lines for all the schools, not just for 15 randomly chosen schools, by plotting the predicted values pred by gndc_verb.
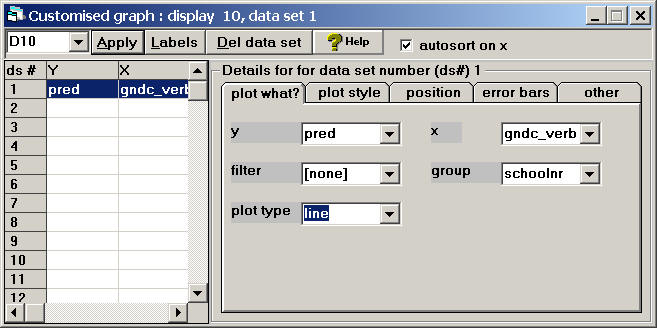
Graphs Customised Graph(s) in the field called y choose pred, for x choose gndc_verb, for group choose schoolnr, and for plot type choose line Click Apply to generate the graph
Creating the variable gndc_gsize which is groupsiz centered around the grand mean and verbXgsize which is the interaction of gndc_gsize and gndc_verb.
Calculate
Choose an unused variable and rename it gndc_gsize by using ctrl+n
Enter "gndc_gsize" = "groupsiz" - 23.1 and click on calculate
Clear the equation window
Choose an unused variable and rename it verbXgsize by using ctrl+n
Enter "verbXgsize" = "gndc_verb"*"gndc_gsize" and click on calculate
Table 5.2, p. 75.
Model with random slopes and cross-level interactions.
Model
Equations
Click on Y
Choose y: langpost, N levels: 2 - ij, level2(j): schoolnr, and
level1(i): pupilnr.
Click on the x0 variable
Choose the variable constant and select both schoolnr and pupilnr.
Add Term
Click on the x1 variable
Choose grpmc_verb as a fixed parameter
Add Term
Click on the x2 variable
Choose gndc_verb as a fixed parameter and as a random slope with variance
at the j(schoolnr) level
Add Term
Click on the x3 variable
Choose gndc_gsize as a fixed parameter
Add Term
Click on the x4 variable
Choose verbXgsize as a fixed parameter
Click on the Start button located below the file menu and then click on estimates at the bottom of the equations window to make the estimates appear.
Page 77, table 5.3 (skipped for now)
Calculating the grand mean for ses and then creating the variable gndc_ses which is centered around the grand mean.
Basic Statistics Averages and Correlations Choose ses and click on calculate.
Calculate Choose an unused variable and rename it gndc_ses by using ctrl+n Enter "gndc_ses" = "ses" - 27.812 and click on calculate.
Creating the variable verbXcomb which is the interaction of gndc_verb and comb.
Calculate Choose an unused variable and rename it verbXcomb by using ctrl+n Enter "verbXcomb" = "gndc_verb"*"comb" and click on calculate.
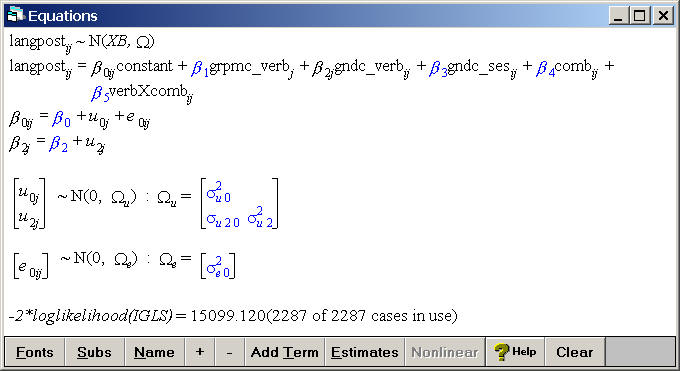
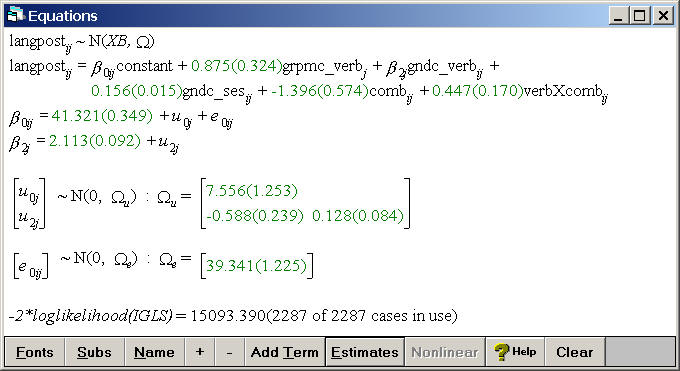
Table 5.4, p. 78
The smaller and more parsimonious model including a random slope and many fixed effects.
Model
Equations
Click on Y
Choose y: langpost, N levels: 2 - ij, level2(j): schoolnr, and
level1(i): pupilnr.
Click on the x0 variable
Choose the variable constant and select both schoolnr and pupilnr.
Add Term
Click on the x1 variable
Choose grpmc_verb as a fixed parameter
Add Term
Click on the x2 variable
Choose gndc_verb as a fixed parameter and as a random slope with variance
at the j(schoolnr) level
Add Term
Click on the x3 variable
Choose gndc_ses as a fixed parameter
Add Term
Click on the x4 variable
Choose comb as a fixed parameter
Add Term
Click on the x5 variable
Choose verbXcomb as a fixed parameter
Click on the Start button located below the file menu and then click on estimates at the bottom of the equations window to make the estimates appear.
Page 84, table 5.5 (we don’t have the data for this example)